Hepatitis B virus-mediated changes of apolipoprotein mRNA abundance in cultured hepatoma cells
- PMID: 12692252
- PMCID: PMC153946
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.9.5503-5506.2003
Hepatitis B virus-mediated changes of apolipoprotein mRNA abundance in cultured hepatoma cells
Abstract
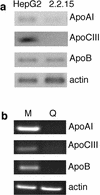
An inverse correlation between hepatitis B virus (HBV) and steady-state levels of apolipoprotein AI and CIII mRNAs was observed in two hepatoma cell lines. Analysis of a third line containing an inducible viral genome implicated viral pregenomic RNA in apolipoprotein mRNA reduction. We conclude that HBV alters infected cells despite the absence of overt cytopathogenicity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Utilization of recombinant adenovirus and dominant negative mutants to characterize hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-regulated apolipoprotein AI and CIII expression.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 23;272(21):13892-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.21.13892. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9153249
-
[The distribution of apolipoproteins AI, CII and CIII mRNA in rat tissues].Hua Xi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 1991 Sep;22(3):232-4. Hua Xi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 1991. PMID: 1748403 Chinese.
-
Cell culture conditions determine apolipoprotein CIII secretion and regulation by fibrates in human hepatoma HepG2 cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 1999;9(3):139-49. doi: 10.1159/000016311. Cell Physiol Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10494028
-
[Interaction between genes and diet as a determinant of the plasma levels of cholesterol].Med Clin (Barc). 1998 Oct 31;111(14):546-51. Med Clin (Barc). 1998. PMID: 9859082 Review. Spanish. No abstract available.
-
[Apolipoprotein A-I, E, C-III and LDL-receptor mRNA expression in liver diseases].Nihon Rinsho. 1993 Feb;51(2):407-13. Nihon Rinsho. 1993. PMID: 8464155 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Low plasma apolipoprotein A-I level is not a reliable marker of fibrosis in children with chronic hepatitis B.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Oct 1;10(19):2864-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2864. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15334687 Free PMC article.
-
Association between hepatitis B and metabolic syndrome: Current state of the art.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 7;22(1):155-64. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.155. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26755867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus inhibits the in vivo and in vitro synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein C3.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Nov 13;16(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0607-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 29132372 Free PMC article.
-
HBV inhibits apoB production via the suppression of MTP expression.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Nov 11;10:207. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-207. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22074108 Free PMC article.
-
Transaminase Elevations during Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: Safety Considerations and Role in Achieving Functional Cure.Viruses. 2021 Apr 23;13(5):745. doi: 10.3390/v13050745. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33922828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beasley, R. P., and L. Y. Hwang. 1994. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma, p. 209-224. In G. N. Vyas, J. L. Dienstag, and J. H. Hoofnagle (ed.), Viral hepatitis and liver disease. Grune and Stratton, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Bréchot, C., D. Gozuacik, Y. Murakami, and P. Paterlini-Bréchot. 2000. Molecular bases for the development of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Semin. Cancer Biol. 10:211-231. - PubMed
-
- Carpentier, Y. A., and O. Scruel. 2002. Changes in the concentration and composition of plasma lipoproteins during the acute phase response. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 5:153-158. - PubMed
-
- Chisari, F. V., and C. Ferrari. 1995. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13:29-60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

