Hepatitis B virus-mediated changes of apolipoprotein mRNA abundance in cultured hepatoma cells
- PMID: 12692252
- PMCID: PMC153946
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.9.5503-5506.2003
Hepatitis B virus-mediated changes of apolipoprotein mRNA abundance in cultured hepatoma cells
Abstract
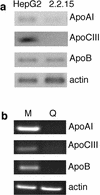
An inverse correlation between hepatitis B virus (HBV) and steady-state levels of apolipoprotein AI and CIII mRNAs was observed in two hepatoma cell lines. Analysis of a third line containing an inducible viral genome implicated viral pregenomic RNA in apolipoprotein mRNA reduction. We conclude that HBV alters infected cells despite the absence of overt cytopathogenicity.
Figures


References
-
- Beasley, R. P., and L. Y. Hwang. 1994. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma, p. 209-224. In G. N. Vyas, J. L. Dienstag, and J. H. Hoofnagle (ed.), Viral hepatitis and liver disease. Grune and Stratton, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Bréchot, C., D. Gozuacik, Y. Murakami, and P. Paterlini-Bréchot. 2000. Molecular bases for the development of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Semin. Cancer Biol. 10:211-231. - PubMed
-
- Carpentier, Y. A., and O. Scruel. 2002. Changes in the concentration and composition of plasma lipoproteins during the acute phase response. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 5:153-158. - PubMed
-
- Chisari, F. V., and C. Ferrari. 1995. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13:29-60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

