The histological features of microwave coagulation therapy: an assessment of a new applicator design
- PMID: 12694484
- PMCID: PMC2517540
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2613.2003.00236.x
The histological features of microwave coagulation therapy: an assessment of a new applicator design
Abstract
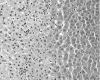
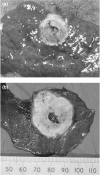
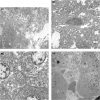
Microwave ablation of tumours within the liver may become an adjunct or alternative to resection in patients with primary or secondary cancers. This technique combines the benefits of a large, localized coagulative effect with a single insertion of the applicator, in a significantly shorter time than comparable treatments. A new range of microwave applicators were developed and tested in animal models and both ex-vivo and in-vivo specimens of human liver at resection. At laparotomy, the applicator tip was inserted into normal liver parenchyma and tumours, with each specimen subjected to irradiation for 180 s or more and at varying power outputs. On sectioning an area of spherical blanching was observed around the applicator cavity. Microscopically a zone of coagulative necrosis was seen adjacent to the site of probe insertion. Damage to blood vessels and bile ducts occurred distal to the probe cavity suggesting the passage of heated fluid, a finding that was diminished by temporary occlusion of the hepatic vasculature (a Pringle manoeuvre). Ultra-structural damage was confirmed within the burn zone and selected liver enzymes were shown to be functioning beyond this region. We suggest this indicates the surrounding liver parenchyma is functioning normally and therefore the volume of microwave-induced damage is controllable. We are confident that the new applicator design will allow the effective treatment of larger tumours in a safe and controlled manner with a single application of energy.
Figures












References
-
- Boon ME, Kok LP. Microwave Cookbook for Pathology. 3. Leiden: Colomb Press; 1989.
-
- Cozzi PJ, Stewart GJ, Morris DL. Thrombocytopenia after hepatic cryotherapy for colorectal metastases: correlates with hepatocellular injury. World J. Surg. 1994;18:774–777. - PubMed
-
- Culling CFA. Handbook of histopathological Techniques. London: Butterworths Publishing; 1963. p. 244.
-
- Dodd GD, III, Soulen MC, Kane RA, Livraghi T, Lees WR, Yamashita Y, Gillams AR, Karahan OI, Rhim H. Minimally invasive treatment of malignant hepatic tumours: At the threshold of a major breakthrough 1. Radiographics. 2000;20:9–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

