External auditory canal cholesteatoma: clinical and imaging spectrum
- PMID: 12695217
- PMCID: PMC8148678
External auditory canal cholesteatoma: clinical and imaging spectrum
Abstract
Background and purpose: Cholesteatoma is an inflammatory lesion of the temporal bone that uncommonly involves the external auditory canal (EAC). In this large case series, we aimed to define its imaging features and to determine the characteristics most important to its clinical management.
Methods: Thirteen cases of EAC cholesteatoma (EACC) were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical data were reviewed for the history, presentation, and physical examination findings. High-resolution temporal bone CT scans were examined for a soft-tissue mass in the EAC, erosion of adjacent bone, and bone fragments in the mass. The middle ear cavity, mastoid, facial nerve canal, and tegmen tympani were evaluated for involvement.
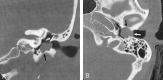
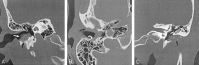
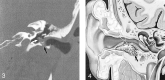
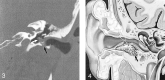
Results: Patients presented with otorrhea, otalgia, or hearing loss. Eight cases were spontaneous, and five were postsurgical or post-traumatic. CT imaging in all 13 cases showed a soft-tissue mass with adjacent bone erosion. Intramural bone fragments were identified in seven cases. This mass most often arose inferiorly (n = 8) or posteriorly (n = 8), but it was circumferential in two cases. We noted middle ear extension (n = 5), mastoid involvement (n = 4), facial canal erosion (n = 2), and tegmen tympani dehiscence (n = 1).
Conclusion: Temporal bone CT shows EACC as a soft-tissue mass within the EAC, with adjacent bone erosion. Bone fragments may be present within the mass. The cholesteatoma may extend into the mastoid or middle ear, or it may involve the facial nerve canal or tegmen tympani. Recognition of this entity and its possible extension is important because it may influence clinical management.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Imaging features and surgical approach of external auditory canal cholesteatoma].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007 Aug;21(16):741-3. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18035739 Chinese.
-
External auditory canal cholesteatoma in children: clinical manifestations.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Dec;281(12):6645-6651. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08892-7. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39133277 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical characteristics and surgical management of extensive cholesteatoma of external auditory canal].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 May;27(10):468-72. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23937009 Chinese.
-
Cholesteatoma in patients with congenital external auditory canal anomalies: retrospective review.J Laryngol Otol. 2011 Nov;125(11):1116-20. doi: 10.1017/S0022215111002052. Epub 2011 Aug 16. J Laryngol Otol. 2011. PMID: 21846418 Review.
-
Giant Cholesteatoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Otol Neurotol. 2022 Jul 1;43(6):e658-e622. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003549. Otol Neurotol. 2022. PMID: 35761458 Review.
Cited by
-
Facial nerve palsy in otitis externa: A red flag?Malays Fam Physician. 2021 Feb 1;16(1):117-120. doi: 10.51866/cr1108. eCollection 2021 Mar 25. Malays Fam Physician. 2021. PMID: 33948150 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging guidance for cholesteatoma surgery using tissue autofluorescence.J Biomed Opt. 2023 Jun;28(6):066003. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.28.6.066003. Epub 2023 Jun 16. J Biomed Opt. 2023. PMID: 37334207 Free PMC article.
-
Primary intracranial cholesteatoma in the thalamus.Surg Neurol Int. 2025 May 16;16:187. doi: 10.25259/SNI_252_2025. eCollection 2025. Surg Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40469356 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical features and surgical treatment of external auditory canal cholesteatoma in 149 cases].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jun;34(6):516-520. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.06.009. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32842182 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Cholesteatoma of the clivus.Skull Base. 2006 Feb;16(1):45-7. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-926218. Skull Base. 2006. PMID: 16880901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anthony PF, Anthony WP. Surgical treatment of external auditory canal cholesteatoma. Laryngoscope 1982;92:70–75 - PubMed
-
- Piepergerdes MC, Kramer BM, Behnke EE. Keratosis obturans and external auditory canal cholesteatoma. Laryngoscope 1980;90:383–391 - PubMed
-
- Holt JJ. Ear canal cholesteatoma. Laryngoscope 1992;102:608–613 - PubMed
-
- Swartz JD, Harnsberger HR. The external auditory canal. In: Imaging of the Temporal Bone. 3rd ed. New York: Thieme;1998. :16–46
-
- Shire JR, Donegan JO. Cholesteatoma of the external auditory canal and keratosis obturans. Am J Otol 1986;7:361–364 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
