Interleukin (IL)-15R[alpha]-deficient natural killer cells survive in normal but not IL-15R[alpha]-deficient mice
- PMID: 12695489
- PMCID: PMC2193874
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021836
Interleukin (IL)-15R[alpha]-deficient natural killer cells survive in normal but not IL-15R[alpha]-deficient mice
Abstract
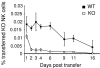
Natural killer (NK) cells protect hosts against viral pathogens and transformed cells. IL-15 is thought to play a critical role in NK cell development, but its role in the regulation of peripheral NK cells is less well defined. We now find that adoptive transfer of normal NK cells into mice lacking the high affinity interleukin (IL)-15 receptor, IL-15Ralpha, surprisingly results in the abrupt loss of these cells. Moreover, IL-15Ralpha-deficient NK cells can differentiate successfully in radiation bone marrow chimera bearing normal cells. Finally, adoptively transferred IL-15Ralpha-deficient NK cells survive in normal but not IL-15Ralpha-deficient mice. These findings demonstrate that NK cell-independent IL-15Ralpha expression is critical for maintaining peripheral NK cells, while IL-15Ralpha expression on NK cells is not required for this function.
Figures
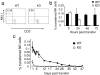

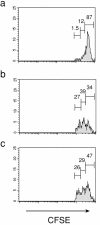

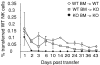
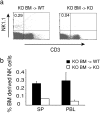
References
-
- Karlhofer, F.M., R.K. Ribaudo, and W.M. Yokoyama. 1992. MHC class I alloantigen specificity of Ly-49+ IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Nature. 358:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Fehniger, T.A., K. Suzuki, J.B. VanDeusen, M.A. Cooper, A.G. Freud, and M.A. Caligiuri. 2001. Fatal leukemia in interleukin-15 transgenic mice. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 27:223–230. - PubMed
-
- Fehniger, T.A., K. Suzuki, A. Ponnappan, J.B. VanDeusen, M.A. Cooper, S.M. Florea, A.G. Freud, M.L. Robinson, J. Durbin, and M.A. Caligiuri. 2001. Fatal leukemia in interleukin 15 transgenic mice follows early expansions in natural killer and memory phenotype CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 193:219–231. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bamford, R.N., A.J. Grant, J.D. Burton, C. Peters, G. Kurys, C.K. Goldman, J. Brennan, E. Roessler, and T.A. Waldmann. 1994. The interleukin (IL) 2 receptor beta chain is shared by IL-2 and a cytokine, provisionally designated IL-T, that stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 91:11:4940–4944. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burton, J.D., R.N. Bamford, C. Peters, A.J. Grant, G. Kurys, C.K. Goldman, J. Brennan, E. Roessler, and T.A. Waldmann. 1994. A lymphokine, provisionally designated interleukin T and produced by a human adult T-cell leukemia line, stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 91:4935–4939. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

