Synapse formation is regulated by the signaling adaptor GIT1
- PMID: 12695502
- PMCID: PMC2172873
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200211002
Synapse formation is regulated by the signaling adaptor GIT1
Abstract
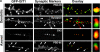
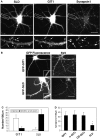
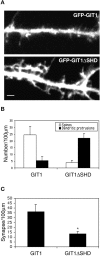
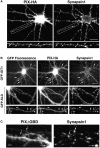
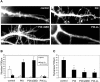
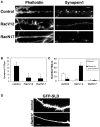
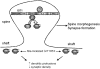
Dendritic spines in the central nervous system undergo rapid actin-based shape changes, making actin regulators potential modulators of spine morphology and synapse formation. Although several potential regulators and effectors for actin organization have been identified, the mechanisms by which these molecules assemble and localize are not understood. Here we show that the G protein-coupled receptor kinase-interacting protein (GIT)1 serves such a function by targeting actin regulators and locally modulating Rac activity at synapses. In cultured hippocampal neurons, GIT1 is enriched in both pre- and postsynaptic terminals and targeted to these sites by a novel domain. Disruption of the synaptic localization of GIT1 by a dominant-negative mutant results in numerous dendritic protrusions and a significant decrease in the number of synapses and normal mushroom-shaped spines. The phenotype results from mislocalized GIT1 and its binding partner PIX, an exchange factor for Rac. In addition, constitutively active Rac shows a phenotype similar to the GIT1 mutant, whereas dominant-negative Rac inhibits the dendritic protrusion formation induced by mislocalized GIT1. These results demonstrate a novel function for GIT1 as a key regulator of spine morphology and synapse formation and point to a potential mechanism by which mutations in Rho family signaling leads to decreased neuronal connectivity and cognitive defects in nonsyndromic mental retardation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A GIT1/PIX/Rac/PAK signaling module regulates spine morphogenesis and synapse formation through MLC.J Neurosci. 2005 Mar 30;25(13):3379-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3553-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15800193 Free PMC article.
-
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Asef2 promotes dendritic spine formation via Rac activation and spinophilin-dependent targeting.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 17;290(16):10295-308. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.605543. Epub 2015 Mar 6. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25750125 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling of PAK-interacting exchange factor PIX to GIT1 promotes focal complex disassembly.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;20(17):6354-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.17.6354-6363.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10938112 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPase signaling at the synapse: implications for intellectual disability.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Sep 10;319(15):2368-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.05.033. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23769912 Review.
-
Expanding functions of GIT Arf GTPase-activating proteins, PIX Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors and GIT-PIX complexes.J Cell Sci. 2016 May 15;129(10):1963-74. doi: 10.1242/jcs.179465. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27182061 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Paxillin phosphorylation at Ser273 localizes a GIT1-PIX-PAK complex and regulates adhesion and protrusion dynamics.J Cell Biol. 2006 May 22;173(4):587-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200509075. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16717130 Free PMC article.
-
A neuron-specific cytoplasmic dynein isoform preferentially transports TrkB signaling endosomes.J Cell Biol. 2008 Jun 16;181(6):1027-39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200803150. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18559670 Free PMC article.
-
Novel putative targets of N-ethylmaleimide sensitive fusion protein (NSF) and alpha/beta soluble NSF attachment proteins (SNAPs) include the Pak-binding nucleotide exchange factor betaPIX.J Cell Biochem. 2006 Nov 1;99(4):1203-15. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20998. J Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16795052 Free PMC article.
-
An APPL1/Akt signaling complex regulates dendritic spine and synapse formation in hippocampal neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Mar;46(3):633-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.01.003. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21236345 Free PMC article.
-
β-Pix modulates actin-mediated recruitment of synaptic vesicles to synapses.J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 23;31(47):17123-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2359-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22114281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, K.M., J.G. Gleeson, S. Bagrodia, M.W. Partington, J.C. MacMillan, R.A. Cerione, J.C. Mulley, and C.A. Walsh. 1998. PAK3 mutation in nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 20:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, A.P., and S.L. Milgram. 2002. Signals from the X: signal transduction and X-linked mental retardation. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 20:397–406. - PubMed
-
- Billuart, P., T. Bienvenu, N. Ronce, V. des Portes, M.C. Vinet, R. Zemni, A. Carrie, C. Beldjord, A. Kahn, C. Moraine, and J. Chelly. 1998. Oligophrenin 1 encodes a rho-GAP protein involved in X-linked mental retardation. Pathol. Biol. (Paris). 46:678. - PubMed
-
- Craig, A.M., and H. Boudin. 2001. Molecular heterogeneity of central synapses: afferent and target regulation. Nat. Neurosci. 4:569–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

