Binding to EGF receptor of a laminin-5 EGF-like fragment liberated during MMP-dependent mammary gland involution
- PMID: 12695504
- PMCID: PMC2172889
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200208145
Binding to EGF receptor of a laminin-5 EGF-like fragment liberated during MMP-dependent mammary gland involution
Abstract
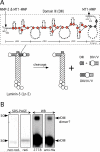
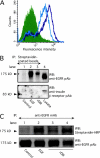
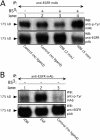
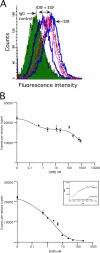
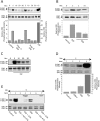
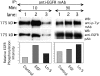
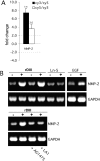
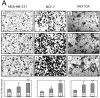
Extracellular matrix (ECM) fragments or cryptic sites unmasked by proteinases have been postulated to affect tissue remodeling and cancer progression. Therefore, the elucidation of their identities and functions is of great interest. Here, we show that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) generate a domain (DIII) from the ECM macromolecule laminin-5. Binding of a recombinant DIII fragment to epidermal growth factor receptor stimulates downstream signaling (mitogen-activated protein kinase), MMP-2 gene expression, and cell migration. Appearance of this cryptic ECM ligand in remodeling mammary gland coincides with MMP-mediated involution in wild-type mice, but not in tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (TIMP-3)-deficient mice, supporting physiological regulation of DIII liberation. These findings indicate that ECM cues may operate via direct stimulation of receptor tyrosine kinases in tissue remodeling, and possibly cancer invasion.
Figures




References
-
- Belkin, A.M., and M.A. Stepp. 2000. Integrins as receptors for laminins. Microsc. Res. Tech. 51:280–301. - PubMed
-
- Bilban, M., L.K. Buehler, S. Head, G. Desoye, and V. Quaranta. 2002. Normalizing DNA microarray data. Curr. Issues. Mol. Biol. 4:57–64. - PubMed
-
- Borradori, L., and A. Sonnenberg. 1999. Structure and function of hemidesmosomes: more than simple adhesion complexes. J. Invest. Dermatol. 112:411–418. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Z., T.B. Gibson, F. Robinson, L. Silvestro, G. Pearson, B. Xu, A. Wright, C. Vanderbilt, and M.H. Cobb. 2001. MAP Kinases. Chem. Rev. 101:2449–2476. - PubMed
-
- Csordas, G., M. Santra, C.C. Reed, I. Eichstetter, D.J. McQuillan, D. Gross, M.A. Nugent, G. Hajnoczky, and R.V. Iozzo. 2000. Sustained down-regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by decorin. A mechanism for controlling tumor growth in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 275:32879–32887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

