Stromelysin-1 and mesothelin are differentially regulated by Wnt-5a and Wnt-1 in C57mg mouse mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 12697065
- PMCID: PMC155645
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213x-3-2
Stromelysin-1 and mesothelin are differentially regulated by Wnt-5a and Wnt-1 in C57mg mouse mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: The Wnt signal transduction pathway is important in a wide variety of developmental processes as well as in the genesis of human cancer. Vertebrate Wnt pathways can be functionally separated into two classes, the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and the non-canonical Wnt/Ca2+ pathway. Supporting differences in Wnt signaling, gain of function of Wnt-1 in C57mg mouse mammary epithelial cells leads to their morphological transformation while loss of function of Wnt-5a leads to the same transformation. Many downstream target genes of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway have been identified. In contrast, little is known about the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway and whether it regulates gene expression.
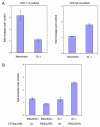
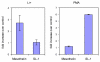
Results: To test the hypothesis that a specific cell line can respond to distinct Wnts with different patterns of gene expression, we over-expressed Wnt-5a and Rfz-2 in C57mg mammary epithelial cells and compared this cell line to C57mg cells over-expressing Wnt-1. These Wnts were chosen since previous studies suggest that C57mg cells respond differently to these Wnts, and since these Wnts can activate different signaling pathways in other systems. Using DNA microarray analysis, we identified several genes that are regulated by Wnt-5a and Rfz-2 as well as by Wnt-1. We then focused on two genes previously linked to various cancers, mesothelin and stromelysin-1, which are respectively up-regulated by Wnt-1 and Wnt-5a in C57mg cells.
Conclusion: Different Wnts have distinct effects on gene expression in a single cell line.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transformation by Wnt family proteins correlates with regulation of beta-catenin.Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Dec;8(12):1349-58. Cell Growth Differ. 1997. PMID: 9419423
-
Regulated expression of Wnt family members during proliferation of C57mg mammary cells.Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Feb;5(2):197-206. Cell Growth Differ. 1994. PMID: 8180133
-
Identification of Wnt responsive genes using a murine mammary epithelial cell line model system.BMC Dev Biol. 2004 May 12;4:6. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-4-6. BMC Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15140269 Free PMC article.
-
New steps in the Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction pathway.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000;55:225-36. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000. PMID: 11036939 Review.
-
WNTs modulate cell fate and behavior during vertebrate development.Trends Genet. 1997 Apr;13(4):157-62. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(97)01093-7. Trends Genet. 1997. PMID: 9097727 Review.
Cited by
-
Biology of Mesothelin and Clinical Implications: A Review of Existing Literature.World J Oncol. 2023 Oct;14(5):340-349. doi: 10.14740/wjon1655. Epub 2023 Sep 20. World J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37869242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in liver cancer antibody therapies: a focus on glypican-3 and mesothelin.BioDrugs. 2011 Oct 1;25(5):275-84. doi: 10.2165/11595360-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2011. PMID: 21942912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Abnormal Methylation of Wnt5a Gene Promoter Regions in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: A Clinical and Experimental Study.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018 Jul 16;2018:6567081. doi: 10.1155/2018/6567081. eCollection 2018. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018. PMID: 30079293 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Adhesion Molecule CD166/ALCAM Functions Within the Crypt to Orchestrate Murine Intestinal Stem Cell Homeostasis.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jan 25;3(3):389-409. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2016.12.010. eCollection 2017 May. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28462380 Free PMC article.
-
Mesothelin as a Signal Pathways and Epigenetic Target in Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;17(7):1118. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071118. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227616 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

