p38alpha isoform Mxi2 binds to extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 mitogen-activated protein kinase and regulates its nuclear activity by sustaining its phosphorylation levels
- PMID: 12697810
- PMCID: PMC153192
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.9.3079-3090.2003
p38alpha isoform Mxi2 binds to extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 mitogen-activated protein kinase and regulates its nuclear activity by sustaining its phosphorylation levels
Abstract
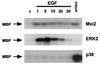
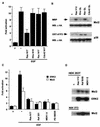
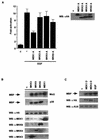
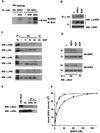
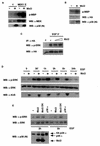
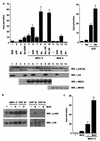
Mxi2 is a p38alpha splice isoform that is distinctively activated by mitogenic stimuli. Here we show that Mxi2 immunoprecipitates carry a kinase activity that is persistently activated by epidermal growth factor in a fashion regulated by Ras, Raf, and MEK. We demonstrate that this kinase activity can be attributed not to Mxi2 but rather to extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), which coimmunoprecipitated with Mxi2 both by ectopic expression and in a physiological environment like the kidney. Furthermore, we provide evidence that Mxi2-ERK interaction has profound effects on ERK function, demonstrating that Mxi2 prolongs the duration of the ERK signal by sustaining its phosphorylation levels. Interestingly, we show that the effects of Mxi2 on ERK are restricted to nuclear events. Mxi2 potently up-regulates ERK-mediated activation of the transcription factors Elk1 and HIF1alpha but has no effect on the activity of ERK cytoplasmic substrates RSK2 and cPLA(2), induced by epidermal growth factor or by MEK. Overall, our findings point to Mxi2 as a unique member of the p38 family that may have an unprecedented role in the regulation of the functions of ERK mitogen-activated protein kinases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Paclitaxel induces prolonged activation of the Ras/MEK/ERK pathway independently of activating the programmed cell death machinery.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 1;276(22):19555-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011164200. Epub 2001 Mar 5. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278851
-
Epidermal growth factor induces c-fos and c-jun mRNA via Raf-1/MEK1/ERK-dependent and -independent pathways in bovine luteal cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2003 Feb 28;200(1-2):141-54. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(02)00379-9. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12644307
-
Interferon-alpha2b reduces phosphorylation and activity of MEK and ERK through a Ras/Raf-independent mechanism.Br J Cancer. 2000 Aug;83(4):532-8. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2000.1263. Br J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10945503 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK)-independent functions of Raf kinases.J Cell Sci. 2002 Apr 15;115(Pt 8):1575-81. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.8.1575. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 11950876 Review.
-
How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is subcellular localization the answer?Cell Cycle. 2009 Apr 15;8(8):1168-75. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.8.8147. Epub 2009 Apr 11. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19282669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of novel human transcript variants by analysis of intronic single-block EST with polyadenylation site.BMC Genomics. 2009 Nov 12;10:518. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-518. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19906316 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct utilization of effectors and biological outcomes resulting from site-specific Ras activation: Ras functions in lipid rafts and Golgi complex are dispensable for proliferation and transformation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jan;26(1):100-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.1.100-116.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16354683 Free PMC article.
-
Mxi2 promotes stimulus-independent ERK nuclear translocation.EMBO J. 2007 Feb 7;26(3):635-46. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601523. Epub 2007 Jan 25. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17255949 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Splicing of MAPKs in the Regulation of Signaling Specificity.Cells. 2021 Dec 8;10(12):3466. doi: 10.3390/cells10123466. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-catenin signaling is required for RAS-driven thyroid cancer through PI3K activation.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):49435-49449. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10356. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27384483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ajenjo, N., D. S. Aaronson, E. Ceballos, C. Richard, J. León, and P. Crespo. 2000. Myeloid leukemia cell growth and differentiation are independent of mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK1/2 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 275:7189-7197. - PubMed
-
- Brunet, A., G. Pages, and J. Pouyssegur. 1994. Growth factor-stimulated MAP kinase induces rapid retrophosphorylation and inhibition of MAP kinase kinase (MEK1). FEBS Lett. 346:299-303. - PubMed
-
- Chen, G., M. Hitom, J. Han, and D. W. Stacey. 2000. The p38 pathway provides negative feedback for Ras proliferative signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 275:38973-38980. - PubMed
-
- Coso, O. A., M. Chiariello, J. C. Yu, H. Teramoto, P. Crespo, N. Xu, T. Miki, and J. S. Gutkind. 1995. Rac-1 and cdc42 control the activity of JNK (SAPK) signaling pathway. Cell 81:1137-1146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
