Transmodulation between phospholipase D and c-Src enhances cell proliferation
- PMID: 12697812
- PMCID: PMC153190
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.9.3103-3115.2003
Transmodulation between phospholipase D and c-Src enhances cell proliferation
Abstract
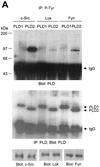
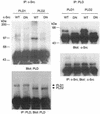
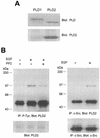
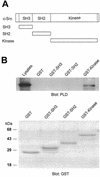
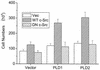
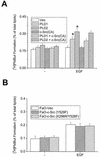
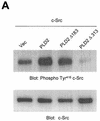
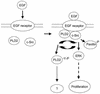
Phospholipase D (PLD) has been implicated in the signal transduction pathways initiated by several mitogenic protein tyrosine kinases. We demonstrate for the first time that most notably PLD2 and to a lesser extent the PLD1 isoform are tyrosine phosphorylated by c-Src tyrosine kinase via direct association. Moreover, epidermal growth factor induced tyrosine phosphorylation of PLD2 and its interaction with c-Src in A431 cells. Interaction between these proteins is via the pleckstrin homology domain of PLD2 and the catalytic domain of c-Src. Coexpression of PLD1 or PLD2 with c-Src synergistically enhances cellular proliferation compared with expression of either molecule. While PLD activity as a lipid-hydrolyzing enzyme is not affected by c-Src, wild-type PLDs but not catalytically inactive PLD mutants significantly increase c-Src kinase activity, up-regulating c-Src-mediated paxillin phosphorylation and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity. These results demonstrate the critical role of PLD catalytic activity in the stimulation of Src signaling. In conclusion, we provide the first evidence that c-Src acts as a kinase of PLD and PLD acts as an activator of c-Src. This transmodulation between c-Src and PLD may contribute to the promotion of cellular proliferation via amplification of mitogenic signaling pathways.
Figures







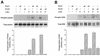
References
-
- Ahn, B. H., H. Rhim, S. Y. Kim, Y. M. Sung, M. Y. Lee, J. Y. Choi, B. Wolozin, J. S. Chang, Y. H. Lee, T. K. Kwon, K. C. Chung, S. H. Yoon, S. J. Hahn, M. S. Kim, Y. H. Jo, and D. S. Min. 2002. α-Synuclein interacts with phospholipase D isozymes and inhibits pervanadate-induced phospholipase D activation in human embryonic kidney-293 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277:12334-12442. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Av, P., and M. Liscovitch. 1989. Phospholipase D activation by the mitogens platelet-derived growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate in NIH-3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 259:64-66. - PubMed
-
- Bjorge, J. D., A. Jakymiw, and D. J. Fujita. 2000. Selected glimpses into the activation and function of Src kinase. Oncogene 19:5620-5635. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. T., and J. A. Cooper. 1996. Regulation, substrates and functions of src. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1287:121-149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
