Cell cycle activation of the Swi6p transcription factor is linked to nucleocytoplasmic shuttling
- PMID: 12697814
- PMCID: PMC153208
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.9.3126-3140.2003
Cell cycle activation of the Swi6p transcription factor is linked to nucleocytoplasmic shuttling
Abstract
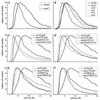
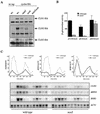
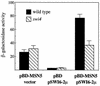
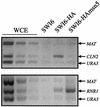
The control of the subcellular localization of cell cycle regulators has emerged as a crucial mechanism in the regulation of cell division. In the present work, we have characterized the function of the karyopherin Msn5p in the control of the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Phenotypic analysis of the msn5 mutant revealed an increase in cell size and a functional interaction between Msn5p and the cell cycle transcription factor SBF (composed of the Swi4p and Swi6p proteins), indicating that Msn5p is involved in Start control. In fact, we have shown that the level of Cln2p protein is drastically reduced in an msn5 mutant. The effect on CLN2 expression is mediated at a transcriptional level, Msn5p being necessary for proper SBF-dependent transcription. On the contrary, loss of MSN5 has no effect on the closely related transcription factor MBF (composed of the Mbp1p and Swi6p proteins). Regulation of SBF by Msn5p is exerted by control of the localization of the regulatory subunit Swi6p. Swi6p shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm during the cell cycle, and we have found that Msn5p is required for Swi6p export from the nucleus during the G(2)-M phase. What is more important, we have demonstrated that export of Swi6p to the cytoplasm is required for SBF activity, providing evidence for a functional switch of Swi6p linked to its nucleocytoplasmic shuttling during the cell cycle.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Karyopherin Msn5 is involved in a novel mechanism controlling the cellular level of cell cycle regulators Cln2 and Swi5.Cell Cycle. 2019 Mar;18(5):580-595. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1578148. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 30739521 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear export of Far1p in response to pheromones requires the export receptor Msn5p/Ste21p.Genes Dev. 1999 Sep 1;13(17):2284-300. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.17.2284. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10485850 Free PMC article.
-
The karyopherin Kap142p/Msn5p mediates nuclear import and nuclear export of different cargo proteins.J Cell Biol. 2001 Feb 19;152(4):729-40. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.4.729. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11266464 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear import of histones.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Dec 18;48(6):2753-2767. doi: 10.1042/BST20200572. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 33300986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of transcription factors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000 Aug;57(8-9):1193-206. doi: 10.1007/pl00000759. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000. PMID: 11028912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The karyopherin Kap95 and the C-termini of Rfa1, Rfa2, and Rfa3 are necessary for efficient nuclear import of functional RPA complex proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.DNA Cell Biol. 2011 Sep;30(9):641-51. doi: 10.1089/dna.2010.1071. Epub 2011 Feb 20. DNA Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21332387 Free PMC article.
-
TFIID and Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase functions probed by genome-wide synthetic genetic array analysis using a Saccharomyces cerevisiae taf9-ts allele.Genetics. 2005 Nov;171(3):959-73. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.046557. Epub 2005 Aug 22. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 16118188 Free PMC article.
-
Exportin-5 orthologues are functionally divergent among species.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(17):4711-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl663. Epub 2006 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16963774 Free PMC article.
-
The CWI Pathway: A Versatile Toolbox to Arrest Cell-Cycle Progression.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Dec 4;7(12):1041. doi: 10.3390/jof7121041. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34947023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whi5 regulation by site specific CDK-phosphorylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2009;4(1):e4300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004300. Epub 2009 Jan 28. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19172996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amon, A., M. Tyers, B. Futcher, and K. Nasmyth. 1993. Mechanisms that help the yeast cell cycle clock tick: G2 cyclins transcriptionally activate G2 cyclins and repress G1 cyclins. Cell 74:993-1007. - PubMed
-
- Bartek, J., J. Bartkova, and J. Lukas. 1996. The retinoblastoma protein pathway and the restriction point. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8:805-814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
