Developmental effects of prenatal cocaine exposure on 5-HT1A receptors in male and female rat offspring
- PMID: 12697990
- PMCID: PMC3111017
- DOI: 10.1159/000069363
Developmental effects of prenatal cocaine exposure on 5-HT1A receptors in male and female rat offspring
Abstract
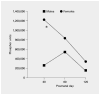
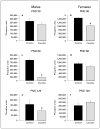
Prenatal cocaine exposure results in behavioral abnormalities throughout development in rats, but little is known regarding the biological mechanisms underlying these abnormalities. Pregnant rats received subcutaneous twice-daily injections (1 ml/kg) of normal saline or 15 mg/kg of cocaine hydrochloride throughout gestation (gestation days 1-20). Following delivery, pups were placed with untreated surrogates. Male and female pups were killed on postnatal days 30, 60 or 120 for assessment of 5-HT(1A) receptor development in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain and pons using radiolabel immunocytochemistry. Findings revealed gender and age differences in developmental regulation of 5-HT(1A) receptors, indicating that male rats are more susceptible to long-term consequences of prenatal cocaine exposure in comparison to females. This study also demonstrates gender-specific development of serotonin (5-HT(1A)) receptors across postnatal ages, demonstrating a fundamentally different pattern of development of 5-HT(1A) receptors between males and females.
Copyright 2002 S. Karger AG, Basel
Figures
References
-
- Akbari HM, Kramer HK, Whitaker-Azmitia PM, Spear LP, Azmitia EC. Prenatal cocaine exposure disrupts the development of the serotonergic system. Brain Res. 1992;572:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Akbari HM, Whitaker-Azmitia PM, Azmitia EC. Prenatal cocaine decreases the trophic factor S-100β and induced microcephaly: Reversal by postnatal 5-HT1A receptor agonists. Neurosci Lett. 1994;170:141–144. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Peled O, Gross-Isseroff R, Ben-Hur H, Hoskins I, Groner Y, Biegon A. Fetal human brain exhibits a prenatal peak in the density of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1991;127:173–176. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Cabrera TM. Potentiation of 5- HT1A receptor-mediated neuroendocrine responses in male but not female rat progeny after prenatal cocaine: Evidence for gender differences. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;271:1453–1461. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Cabrera TM, Van De Kar LD. Prenatal cocaine exposure potentiates 5-HT(2a) receptor function in male and female rat offspring. Synapse. 2000;35:163–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

