Potential use of Sox9 gene therapy for intervertebral degenerative disc disease
- PMID: 12698117
- PMCID: PMC4123440
Potential use of Sox9 gene therapy for intervertebral degenerative disc disease
Abstract
Study design: A new recombinant adenoviral vector expressing Sox9, a chondrocyte-specific transcription factor, was tested in a chondroblastic cell line and primary human intervertebral disc cells in vitro. Direct infection of intervertebral disc cells then was assessed in a rabbit model.
Objectives: To deliver a potentially therapeutic viral vector expressing Sox9 to degenerative human and rabbit intervertebral discs cells, and to assess the effect of Sox9 expression on Type 2 collagen production.
Summary of the background data: The concentration of competent Type 2 collagen, an essential constituent of the healthy nucleus pulposus, declines with intervertebral disc degeneration. Recent studies suggest that Sox9 upregulates Type 2 collagen production. Interventions that augment Type 2 collagen production by intervertebral disc cells may represent a novel therapeutic method for patients with degenerative disc disease.
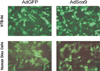
Methods: Adenoviral delivery vectors expressing Sox9 and green fluorescent protein were constructed using the AdEasy system. The chondroblastic cell line, HTB-94, and cultured human degenerated intervertebral disc cells were infected with the vectors. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical analyses were performed to document increased Type 2 collagen expression. The AdSox9 virus then was injected directly into the intervertebral discs of three rabbits. After 5 weeks, the injected discs were evaluated histologically.
Results: The AdSox9 virus efficiently transduced HTB-94 cells and degenerated human disc cells. Western blot analysis confirmed increased Sox9 production. Increased Type 2 collagen production was demonstrated in infected HTB-94 and human disc cells using both reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical staining. In the rabbit model, cells infected with AdSox9 maintained a chondrocytic phenotype, and the architecture of the nucleus pulposus was preserved over a 5-week study period compared to control discs.
Conclusions: A novel adenoviral vector efficiently increased Sox9 and Type 2 collagen synthesis in cultured chondroblastic cells and human degenerated disc cells. In a rabbit model, sustained Sox9 production preserved the histologic appearance of the nucleus pulposus cells in vivo. These findings suggest a potential role for Sox9 gene therapy in the treatment of human degenerative disc disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: No funds were received in support of this work. No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Borenstein D. Epidemiology, etiology, diagnostic evaluation, and treatment of low back pain. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1992;4:226–232. - PubMed
-
- Frymoyer JW, Cats-Baril WL. An overview of the incidences and costs of low back pain. Orthop Clin North Am. 1991;22:263–271. - PubMed
-
- Webster BS, Snook SH. The cost of 1989 workers’ compensation low back pain claims. Spine. 1994;19:1111–1115. discussion 1116. - PubMed
-
- Buckwalter JA. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 1995;20:1307–1314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

