5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA), a novel antivascular agent: phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study
- PMID: 12698178
- PMCID: PMC2747563
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600885
5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA), a novel antivascular agent: phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study
Abstract
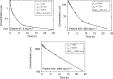
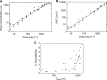
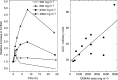
The purpose of this phase I, dose-escalation study was to determine the toxicity, maximum tolerated dose, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamic end points of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone acetic acid (DMXAA). In all, 46 patients received a total of 247 infusions of DMXAA over 15 dose levels ranging from 6 to 4900 mg x m(-2). The maximum tolerated dose was established at 3700 mg x m(-2); dose-limiting toxicities in the form of urinary incontinence, visual disturbance, and anxiety were observed at the highest dose level (4900 mg x m(-2)). The pharmacokinetics of DMXAA were dose dependent. Peak concentrations and area under the curve level increased from 4.8 microM and 3.2 microM h, respectively, at 6 mg x m(-2) to 1290 microM and 7600 microM h at 3700 mg x m(-2), while clearance declined from 7.4 to 1.7 l h(-1) x m(-2) over the same dose range. The terminal half-life was 8.1+/-4.3 h. More than 99% of the drug was protein bound at doses up to 320 mg x m(-2); at higher doses the percent free drug increased to a maximum of 6.9% at 4900 mg x m(-2). Dose-dependent increases in the serotonin metabolite 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid were observed at dose levels of 650 mg x m(-2) and above. There was one unconfirmed partial response at 1300 mg x m(-2). In conclusion, DMXAA is a novel vascular targeting agent and is well tolerated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model of the vascular-disrupting agent 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid in cancer patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Apr 1;14(7):2102-10. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1475. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18381951 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical aspects of a phase I trial of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA), a novel antivascular agent.Br J Cancer. 2003 Jun 16;88(12):1844-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600992. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12799625 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics of 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (AS1404), a novel vascular disrupting agent, in phase I clinical trial.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007 Apr;59(5):681-7. doi: 10.1007/s00280-006-0322-6. Epub 2006 Sep 23. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17021822 Clinical Trial.
-
5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA): a new biological response modifier for cancer therapy.Invest New Drugs. 2002 Aug;20(3):281-95. doi: 10.1023/a:1016215015530. Invest New Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12201491 Review.
-
Predicting pharmacokinetics and drug interactions in patients from in vitro and in vivo models: the experience with 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA), an anti-cancer drug eliminated mainly by conjugation.Drug Metab Rev. 2002 Nov;34(4):751-90. doi: 10.1081/dmr-120015693. Drug Metab Rev. 2002. PMID: 12487149 Review.
Cited by
-
First-in-human phase 1 study of an orally bioavailable vascular-disrupting agent DX1002 in patients with advanced solid tumors.Cell Rep Med. 2025 Feb 18;6(2):101969. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.101969. Cell Rep Med. 2025. PMID: 39970877 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nanoparticle delivered vascular disrupting agents (VDAs): use of TNF-alpha conjugated gold nanoparticles for multimodal cancer therapy.Mol Pharm. 2013 May 6;10(5):1683-94. doi: 10.1021/mp300505w. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Mol Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23544801 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the involvement of p38 MAP kinase in the action of the vascular disrupting agent 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA).Invest New Drugs. 2007 Jun;25(3):271-6. doi: 10.1007/s10637-006-9029-0. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Invest New Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17203401
-
Translational research in phase I trials.Clin Transl Oncol. 2009 Sep;11(9):580-8. doi: 10.1007/s12094-009-0408-9. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19775997 Review.
-
Trial watch: STING agonists in cancer therapy.Oncoimmunology. 2020 Jun 16;9(1):1777624. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1777624. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 32934881 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baguley BC, Cole G, Thomsen LL, Zhuang L (1993) Serotonin involvement in the antitumour and host effects of flavone-8-acetic acid and 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 3: 77–81 - PubMed
-
- Baguley BC, Zhuang L, Kestell P (1997) Increased plasma serotonin following treatment with flavone-8-acetic acid, 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid, vinblastine, and colchicine: relation to vascular effects. Oncology Res 9: 55–60 - PubMed
-
- Chaplin DJ, Pettit GR, Hill SA (1999) Anti-vascular approaches to solid tumour therapy: evaluation of combretastatin A4 phosphate. Anticancer Res 19: 189–195 - PubMed
-
- Ching LM, Joseph WR, Zhuang L, Baguley BC (1994) Induction of tumour necrosis factor-alpha messenger RNA in human and murine cells by the flavone acetic acid analogue 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (NSC 640488). Cancer Res 54: 870–872 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources