IL-1beta-induced Langerhans' cell migration and TNF-alpha production in human skin: regulation by lactoferrin
- PMID: 12699428
- PMCID: PMC1808708
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02146.x
IL-1beta-induced Langerhans' cell migration and TNF-alpha production in human skin: regulation by lactoferrin
Abstract
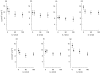
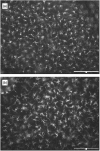
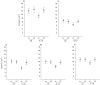
In mice, the roles of cytokines in the initiation of epidermal Langerhans' cell (LC) migration are well documented; however, the mechanism of this response in humans is less well defined. The purpose of the present investigation was to examine the contribution of interleukin (IL)-1beta to human epidermal LC migration and to define further the mechanisms of this response. We demonstrate here that homologous recombinant IL-1beta administered intradermally to healthy human volunteers provides a stimulus for LC migration, with significant (P < 0.01) reductions in LC densities being observed at both 2 h and 4 h following treatment. At the later time-point of 4 h, injection of IL-1beta was also accompanied by activation of those LC remaining in the epidermis. Analysis of fluid aspirated from suction blisters formed at injection sites revealed significant (P < 0.01) tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production (2.99 +/- 1.18 pg TNF-alpha/mg protein; mean +/- s.d. of n = 10) in response to IL-1beta treatment compared with saline control injections (0.90 +/- 1.05 pg TNF-alpha/mg protein). Prior topical application of human recombinant lactoferrin (LF), an iron-binding protein found in exocrine secretions and skin, inhibited IL-1beta-mediated LC migration and also compromised the production of TNF-alpha protein as measured in suction blister fluids derived from each of the treatment sites. Taken together, these data demonstrate that IL-1beta is associated with both the stimulation of human epidermal LC migration and local TNF-alpha production. Topical treatment with LF compromises both these responses. These data suggest that topical LF may potentially represent a novel therapeutic in the treatment of skin inflammation where TNF-alpha is an important mediator.
Figures
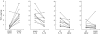
Similar articles
-
Lactoferrin: influences on Langerhans cells, epidermal cytokines, and cutaneous inflammation.Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;80(1):103-7. doi: 10.1139/o01-227. Biochem Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11911118
-
Regulation of epidermal Langerhans cell migration by lactoferrin.Immunology. 2000 May;100(1):21-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00014.x. Immunology. 2000. PMID: 10809955 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of cytokine expression and Langerhans cell migration in human skin following suction blister formation.Exp Dermatol. 2004 Jul;13(7):452-60. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-6705.2004.00199.x. Exp Dermatol. 2004. PMID: 15217366
-
Stimulation of Langerhans cell migration by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha).J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Nov;99(5):48S-50S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12668986. J Invest Dermatol. 1992. PMID: 1431209 Review.
-
Cytokines and Langerhans cell mobilisation in mouse and man.Cytokine. 2005 Oct 21;32(2):67-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2005.07.011. Epub 2005 Sep 8. Cytokine. 2005. PMID: 16153855 Review.
Cited by
-
Release of IL-1beta via IL-1beta-converting enzyme in a skin dendritic cell line exposed to 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene.Mediators Inflamm. 2005 Aug 14;2005(3):131-8. doi: 10.1155/MI.2005.131. Mediators Inflamm. 2005. PMID: 16106098 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Langerhans cell migration in psoriasis.J Exp Med. 2006 Apr 17;203(4):953-60. doi: 10.1084/jem.20052367. Epub 2006 Mar 27. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16567387 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of dendritic cell maturation in the skin microenvironment by soluble factors derived from colon carcinoma.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(6):1622-32. doi: 10.4161/hv.28548. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 24732313 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional iron bound lactoferrin and nanomedicinal approaches to enhance its bioactive functions.Molecules. 2015 May 26;20(6):9703-31. doi: 10.3390/molecules20069703. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26016555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunostimulant patch enhances immune responses to influenza virus vaccine in aged mice.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(14):7610-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7610-7618.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15220436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kimber I, Cumberbatch M, Dearman RJ, et al. Cytokines and chemokines in the initiation and regulation of epidermal Langerhans cell mobilization. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:401–12. - PubMed
-
- Jakob T, Ring CA, Udey MC. Multistep navigation of Langerhans/dendritic cells in and out of the skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:688–96. - PubMed
-
- Cumberbatch M, Dearman RJ, Kimber I. Interleukin 1β and the stimulation of Langerhans cell migration: comparisons with tumour necrosis factor α. Arch Derm Res. 1997a;289:277–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

