Heteromeric HCN1-HCN4 channels: a comparison with native pacemaker channels from the rabbit sinoatrial node
- PMID: 12702747
- PMCID: PMC2342966
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.027698
Heteromeric HCN1-HCN4 channels: a comparison with native pacemaker channels from the rabbit sinoatrial node
Abstract
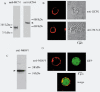
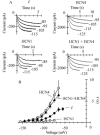
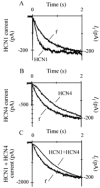
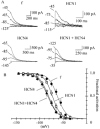
'Funny-' (f-) channels of cardiac sino-atrial node (SAN) cells are key players in the process of pacemaker generation and mediate the modulatory action of autonomic transmitters on heart rate. The molecular components of f-channels are the hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels. Of the four HCN isoforms known, two (HCN4 and HCN1) are expressed in the rabbit SAN at significant levels. However, the properties of f-channels of SAN cells do not conform to specific features of the two isoforms expressed locally. For example, activation kinetics and cAMP sensitivity of native pacemaker channels are intermediate between those reported for HCN1 and HCN4. Here we have explored the possibility that both HCN4 and HCN1 isoforms contribute to the native If in SAN cells by co-assembling into heteromeric channels. To this end, we used heterologous expression in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells to investigate the kinetics and cAMP response of the current generated by co-transfected (HCN4 + HCN1) and concatenated (HCN4-HCN1 (4-1) tandem or HCN1-HCN4 (1-4) tandem) rabbit constructs and compared them with those of the native f-current from rabbit SAN. 4-1 tandem, but not co-transfected, currents had activation kinetics approaching those of If; however, the activation range of 4-1 tandem channels was more negative than that of the f-channel and their cAMP sensitivity were poorer (although that of 1-4 tandem channels was normal). Co-transfection of 4-1 tandem channels with minK-related protein 1(MiRP1) did not alter their properties. HCN1 and HCN4 may contribute to native f-channels, but a 'context'-dependent mechanism is also likely to modulate the channel properties in native tissues.
Figures
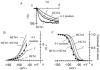
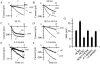


References
-
- Accili EA, Di Francesco D. Inhibition of the hyperpolarization-activated current (If) of rabbit SA node myocytes by niflumic acid. Pflugers Arch. 1996;431:757–762. - PubMed
-
- Accili EA, Proenza C, Baruscotti M, Di Francesco D. From funny current to HCN channels: 20 years of excitation. News Physiol Sci. 2002;17:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Accili EA, Robinson RB, Di Francesco D. Properties and modulation of If in newborn versus adult cardiac SA node. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:H1549–1552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

