Mycobacterium tuberculosis glycosylated phosphatidylinositol causes phagosome maturation arrest
- PMID: 12702770
- PMCID: PMC154363
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0737613100
Mycobacterium tuberculosis glycosylated phosphatidylinositol causes phagosome maturation arrest
Abstract
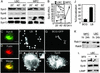
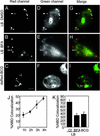
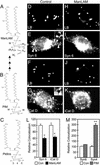
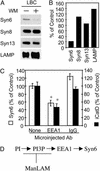
The tubercle bacillus parasitizes macrophages by inhibiting phagosome maturation into the phagolysosome. This phenomenon underlies the tuberculosis pandemic involving 2 billion people. We report here how Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes phagosome maturation arrest. A glycosylated M. tuberculosis phosphatidylinositol [mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan (ManLAM)] interfered with the phagosomal acquisition of the lysosomal cargo and syntaxin 6 from the trans-Golgi network. ManLAM specifically inhibited the pathway dependent on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate-binding effectors. These findings identify ManLAM as the M. tuberculosis product responsible for the inhibition of phagosomal maturation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

