Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan expression and binding of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes in the human placenta during pregnancy
- PMID: 12704116
- PMCID: PMC153269
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2455-2461.2003
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan expression and binding of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes in the human placenta during pregnancy
Abstract
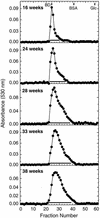
A characteristic feature of malaria during pregnancy is the sequestration of Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells (IRBCs) in the intervillous spaces of the placenta. We have recently shown that unusually low-sulfated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) present in the intervillous spaces mediate the adherence of IRBCs in the placenta. In areas of endemicity, the prevalence of P. falciparum infection in pregnant women peaks during weeks 13 to 20 and then gradually declines, implying that the placental CSPGs are available for IRBC adhesion early during the pregnancy. However, there is no information on the expression and composition of CSPGs during pregnancy. In this study, the expression pattern of CSPGs during the course of pregnancy was investigated. The CSPGs were purified from placentas of various gestational ages, characterized, and tested for the ability to bind IRBCs. The data demonstrate that the CSPGs are present in the intervillous spaces throughout the second and third trimesters. The levels of CSPGs expressed per unit tissue weight were similar in placentas of various gestational ages. However, the structures of the intervillous-space CSPGs changed considerably during the course of pregnancy. In particular, the molecular weight was decreased, with an accompanying gradual increase in the CSPG size polydispersity, from 16 weeks until 38 weeks. The sulfate content was increased considerably after 24 weeks. Despite these structural changes, the CSPGs of placentas of various gestational ages efficiently supported the binding of IRBCs. These results demonstrate that CSPGs can mediate the sequestration of IRBCs in the intervillous spaces of the placenta during the entire second and third trimesters and possibly during the later part of the first trimester as well.
Figures


References
-
- Achur, R. N., M. Valiyaveettil, and D. C. Gowda. The low sulfated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans of human placenta have sulfate group-clustered domains that can efficiently bind Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem., in press. - PubMed
-
- Achur, R. N., M. Valiyaveettill, A. Alkhalil, C. F. Ockenhouse, and D. C. Gowda. 2000. Characterization of proteoglycans of human placenta and identification of unique chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan of the intervillous spaces that mediates the adherence of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes to the placenta. J. Biol. Chem. 275:40344-40356. - PubMed
-
- Alkhalil, A., R. N. Achur, M. Valiyaveettil, C. F. Ockenhouse, and D. C. Gowda. 2000. Structural requirements for the adherence of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes to chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans of human placenta. J. Biol. Chem. 275:40357-40364. - PubMed
-
- Baird, J. K. 1995. Host age as a determinant of naturally acquired immunity to Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Parasitol. Today 11:105-111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

