Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin L
- PMID: 12704169
- PMCID: PMC153286
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2916-2919.2003
Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin L
Abstract
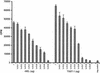
Staphylococcus aureus causes a wide variety of diseases. Major virulence factors of this organism include enterotoxins (SEs) that cause both food poisoning and toxic shock syndrome. Recently, a novel SE, tentatively designated SEL, was identified in a pathogenicity island from a bovine mastitis isolate. The toxin had a molecular weight of 26,000 and an isoelectric point of 8.5. Recombinant SEL shared many biological activities with SEs, including superantigenicity, pyrogenicity, enhancement of endotoxin shock, and lethality in rabbits when administered in subcutaneous miniosmotic pumps, but the protein lacked emetic activity. T cells bearing the T-cell receptor beta chain variable regions 5.1, 5.2, 6.7, 16, and 22 were significantly stimulated by recombinant SEL.
Figures
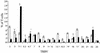
Similar articles
-
Biochemical and biological properties of Staphylococcal enterotoxin K.Infect Immun. 2001 Jan;69(1):360-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.360-366.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11119525 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel staphylococcal enterotoxin-like superantigen, a member of the group V subfamily of pyrogenic toxins.Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 26;41(47):14033-40. doi: 10.1021/bi025977q. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12437361
-
Food poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Jul;2(7):1751-73. doi: 10.3390/toxins2071751. Epub 2010 Jul 5. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity in Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins.Chem Immunol Allergy. 2007;93:24-41. doi: 10.1159/000100856. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2007. PMID: 17369698 Review.
-
Identification and characterization of staphylococcal enterotoxin types G and I from Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 1998 Jul;66(7):3337-48. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.7.3337-3348.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9632603 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic variation among Staphylococcus aureus strains from Norwegian bulk milk.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Dec;71(12):8352-61. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.12.8352-8361.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16332822 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of enterotoxin genes of Staphylococcus SP isolated from nasal cavities and hands of food handlers.Braz J Microbiol. 2010 Jan;41(1):59-65. doi: 10.1590/S1517-838220100001000011. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Braz J Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 24031464 Free PMC article.
-
Emetic potentials of newly identified staphylococcal enterotoxin-like toxins.Infect Immun. 2013 Oct;81(10):3627-31. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00550-13. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23876808 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus superantigens elicit redundant and extensive human Vbeta patterns.Infect Immun. 2009 May;77(5):2043-50. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01388-08. Epub 2009 Mar 2. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19255190 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcal aureus Enterotoxin C and Enterotoxin-Like L Associated with Post-partum Mastitis.Front Microbiol. 2017 Feb 7;8:173. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00173. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28223977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hovde, C. J., J. C. Marr, M. L. Hoffmann, S. P. Hackett, Y. I. Chi, K. K. Crum, D. L. Stevens, C. V. Stauffacher, and G. A. Bohach. 1994. Investigation of the role of the disulphide bond in the activity and structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin C1. Mol. Microbiol. 13:897-909. - PubMed
-
- Laemmli, U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680-685. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL36577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL036577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR041256/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR41256/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000166/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI2840/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR15587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI022159/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 159/PHS HHS/United States
- RR00166/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL37260/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL037260/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI022159/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007421/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

