Activation of heat shock transcription factor 1 in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 12707051
- PMCID: PMC1851193
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64301-5
Activation of heat shock transcription factor 1 in atherosclerosis
Abstract
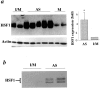
Previous work established that increased expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs) in the vessel wall might evoke proinflammatory and autoimmune reactions in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. The present study was designed to further scrutinize the molecular mechanisms of HSP expression involving activation of heat shock transcription factors (HSFs) in atherosclerotic lesions in animal models. Severe atherosclerotic lesions developed in the aortas of rabbits 16 weeks after feeding a 0.2% cholesterol diet. When protein extracts from the aortas were subjected to Western blot analysis, the level of HSF1 in proteins from atherosclerotic lesions of hypercholesterolemic rabbits were significantly higher than those of normal vessels. Gel mobility shift assays revealed the formation of protein-heat shock element complexes containing HSF1 in protein extracts from atherosclerotic lesion. Furthermore, triglyceride-rich lipoprotein, oxidized-triglyceride-rich lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, and oxidized low-density lipoprotein did not activate HSF1 in cultured smooth muscle cells, whereas HSF1 was highly activated in cells treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Interestingly, mechanical stretching of smooth muscle cells resulted in HSF1 translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and hyperphosphorylation followed by increased HSP70 expression. Thus, our findings provide the first evidence that HSF1 is activated and highly expressed in atherosclerotic lesions and that cytokine stimulation and disturbed mechanical stress to the vessel wall may be responsible for such activation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Enhanced expression of heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) and heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) activation in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Differential regulation of hsp70 expression and hsf1 activation in synovial fibroblasts by proinflammatory cytokines, shear stress, and antiinflammatory drugs.J Clin Invest. 1998 Jul 15;102(2):302-11. doi: 10.1172/JCI2465. J Clin Invest. 1998. PMID: 9664071 Free PMC article.
-
Immunology of atherosclerosis. Demonstration of heat shock protein 60 expression and T lymphocytes bearing alpha/beta or gamma/delta receptor in human atherosclerotic lesions.Am J Pathol. 1993 Jun;142(6):1927-37. Am J Pathol. 1993. PMID: 8099471 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB signaling pathway is inhibited by heat shock independently of active transcription factor HSF1 and increased levels of inducible heat shock proteins.Genes Cells. 2011 Dec;16(12):1168-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2011.01560.x. Epub 2011 Nov 13. Genes Cells. 2011. PMID: 22077664
-
Role of heat shock proteins in atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002 Oct 1;22(10):1547-59. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.0000029720.59649.50. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12377729 Review.
-
Proteotoxic stress response in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Emerging role of heat shock factor 1.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Apr 3;10:1155444. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1155444. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37077734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glutamine-mediated dual regulation of heat shock transcription factor-1 activation and expression.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 23;287(48):40400-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410712. Epub 2012 Oct 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23055521 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell profiling reveals heterogeneity and functional patterning of GPCR expression in the vascular system.Nat Commun. 2017 Jun 16;8:15700. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15700. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28621310 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock factor-1 knockout enhances cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) and multidrug transporter (MDR1) gene expressions to attenuate atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Jul 1;111(1):74-83. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw094. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2016. PMID: 27131506 Free PMC article.
-
CD36 signaling inhibits the translation of heat shock protein 70 induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein through activation of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma.Exp Mol Med. 2008 Dec 31;40(6):658-68. doi: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.6.658. Exp Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 19116451 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DAMPs and altered mitochondrial dynamics in OxLDL burden in atherosclerosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Apr;476(4):1915-1928. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04061-0. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33492610 Review.
References
-
- Ross R: Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 1999, 340:115-126 - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK, Libby P, Schonbeck U, Yan ZQ: Innate and adaptive immunity in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 2002, 91:281-291 - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK: Immune mechanisms in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001, 21:1876-1890 - PubMed
-
- Metzler B, Xu Q: The role of mast cells in atherosclerosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 1997, 114:10-14 - PubMed
-
- Bobryshev YV, Lord RS, Rainer S, Jamal OS, Munro VF: Vascular dendritic cells and atherosclerosis. Pathol Res Pract 1996, 192:462-467 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

