Involvement of avidity for major histocompatibility complex in homeostasis of naive and memory T cells
- PMID: 12707300
- PMCID: PMC2193871
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021812
Involvement of avidity for major histocompatibility complex in homeostasis of naive and memory T cells
Abstract
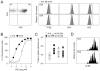
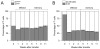
The requirements for survival and self-renewal of peripheral T cells and the nature of mechanisms controlling the size of the naive and memory pool are not completely understood. Here, we examine the involvement of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) in survival and homeostatic expansion of naive and memory T cells. We show that the homeostatic behavior of naive T cell receptor (TCR)-transgenic T cells can be deduced by the expression levels of TCR and CD5, a negative regulator of TCR signaling. Both these factors determine the strength of TCR stimulation by MHC-derived signals. We further show that, similarly to naive T cells, MHC-derived signals influence the homeostatic expansion capacity of memory T cells under lymphopenic conditions. In contrast to naive T cells, however, memory T cells can reach a homeostatic equilibrium, in which survival/self-renewal of each clone is dissociated from their avidity for MHC-derived signals.
Figures

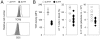



References
-
- Freitas, A.A., and B. Rocha. 2000. Population biology of lymphocytes: the flight for survival. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:83–111. - PubMed
-
- Raff, M.C. 1992. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 356:397–400. - PubMed
-
- Takeda, S., H.R. Rodewald, H. Arakawa, H. Bluethmann, and T. Shimizu. 1996. MHC class II molecules are not required for survival of newly generated CD4+ T cells, but affect their long-term life span. Immunity. 5:217–228. - PubMed
-
- Tanchot, C., F.A. Lemonnier, B. Perarnau, A.A. Freitas, and B. Rocha. 1997. Differential requirements for survival and proliferation of CD8 naive or memory T cells. Science. 276:2057–2062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

