Control of axon elongation via an SDF-1alpha/Rho/mDia pathway in cultured cerebellar granule neurons
- PMID: 12707308
- PMCID: PMC2172896
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200210149
Control of axon elongation via an SDF-1alpha/Rho/mDia pathway in cultured cerebellar granule neurons
Abstract
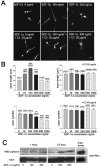
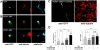
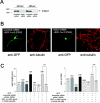
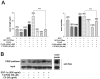
Rho-GTPase has been implicated in axon outgrowth. However, not all of the critical steps controlled by Rho have been well characterized. Using cultured cerebellar granule neurons, we show here that stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1alpha, a neural chemokine, is a physiological ligand that can turn on two distinct Rho-dependent pathways with opposite consequences. A low concentration of the ligand stimulated a Rho-dependent pathway that mediated facilitation of axon elongation. In contrast, Rho/ROCK activation achieved by a higher concentration of SDF-1alpha caused repression of axon formation and induced no more increase in axon length. However, even at this higher concentration a Rho-dependent axon elongating activity could be recovered upon removal of ROCK activity using Y-27632. SDF-1alpha-induced axon elongating activity under ROCK inhibition was replicated by the dominant-active form of the mammalian homologue of the Drosophila gene Diaphanous (mDia)1 and counteracted by its dominant-negative form. Furthermore, RNAi knockdown of mDia1 abolished SDF-1alpha-induced axon elongation. Together, our results support a critical role for an SDF-1alpha/Rho/mDia1 pathway in mediating axon elongation.
Figures






References
-
- Altman, J., and S.A. Bayer. 1996. The third stage of cerebellar development: maturation of the cerebellar system. Development of the Cerebellar System. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. 324–469.
-
- Bito, H., K. Deisseroth, and R.W. Tsien. 1996. CREB phosphorylation and dephosphorylation: a Ca2+- and stimulus duration-dependent switch for hippocampal gene expression. Cell. 87:1203–1214. - PubMed
-
- Bito, H., T. Furuyashiki, H. Ishihara, Y. Shibasaki, K. Ohashi, K. Mizuno, M. Maekawa, M. Ishizaki, and S. Narumiya. 2000. A critical role for a Rho-associated kinase, p160ROCK, in determining axon outgrowth in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuron. 26:431–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

