CB(1) cannabinoid receptor antagonism promotes remodeling and cannabinoid treatment prevents endothelial dysfunction and hypotension in rats with myocardial infarction
- PMID: 12711625
- PMCID: PMC1573770
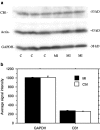
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705156
CB(1) cannabinoid receptor antagonism promotes remodeling and cannabinoid treatment prevents endothelial dysfunction and hypotension in rats with myocardial infarction
Abstract
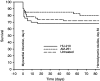
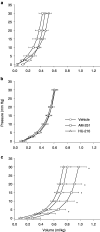
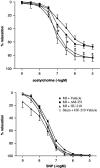
1. To study the long-term effects of altered cannabinoid receptor activity on myocardial and vascular function, Wistar rats were treated with the selective CB(1) antagonist AM-251 (0.5 mg kg(-1) d(-1)), the potent synthetic cannabinoid HU-210 (50 micro g kg(-1) d(-1)) or vehicle for 12 weeks after coronary artery ligation or sham operation. 2. AM-251 further reduced the pressure-generating capacity, shifted the pressure volume curve to the right (P<0.05) and increased the left-ventricular operating volume (AM-251: 930+/-40 micro l vs control: 820+/-40 micro l vs HU-210: 790+/-50 micro l; P<0.05) in rats with large myocardial infarction (MI). 3. Left-ventricular CB(1) immunoactivity in rats 12 weeks after large MI was unaltered as compared with noninfarcted hearts. 4. Cannabinoid receptor activation through HU-210, a cannabinoid that alters cardiovascular parameters via CB(1) receptors, increased the left-ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP, P<0.05). However, it prevented the drop in left-ventricular systolic pressure (HU-210: 142+/-5 mm Hg; P<0.05 vs control: 124+/-3 mm Hg; and P<0.001 vs AM-251: 114+/-3 mm Hg) and prevented endothelial dysfunction (ED) in aortic rings of rats with large MI (P<0.05). 5. Compared with AM-251, HU-210 prevented the decline in the maximal rate of rise of left-ventricular pressure and the maximum pressure-generating ability (P<0.05). In rats with small MI, HU-210 increased cardiac index (P<0.01) and lowered the total peripheral resistance (P<0.05). 6. The study shows that during the development of congestive heart failure post-large MI, cannabinoid treatment increases LVEDP and prevents hypotension and ED. Presumed CB(1) antagonism promotes remodeling despite unchanged myocardial CB(1) expression.
Figures
Comment in
-
Endocannabinoids as mediators in the heart: a potential target for therapy of remodelling after myocardial infarction?Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;138(7):1183-4. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705155. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12711614 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Combined effects of ramipril and angiotensin II receptor blocker TCV116 on rat congestive heart failure after myocardial infarction.Chin Med J (Engl). 2005 Jan 20;118(2):146-54. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. PMID: 15667801
-
Central infusion of aldosterone synthase inhibitor attenuates left ventricular dysfunction and remodelling in rats after myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Res. 2009 Feb 15;81(3):574-81. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn222. Epub 2008 Aug 8. Cardiovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 18689429
-
Improvement in left ventricular remodeling by the endothelial nitric oxide synthase enhancer AVE9488 after experimental myocardial infarction.Circulation. 2008 Aug 19;118(8):818-27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.717702. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18678774
-
[Function of cannabinoids in heart failure].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2008 May 8;62:174-84. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2008. PMID: 18464680 Review. Polish.
-
[Cardiac and vascular effects of cannabinoids: toward a therapeutic use?].Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2005 Mar;54(2):89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ancard.2004.11.011. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2005. PMID: 15828464 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Role of cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system in modulation of diabetic cardiomyopathy.World J Diabetes. 2022 May 15;13(5):387-407. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387. World J Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35664549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Why Do Marijuana and Synthetic Cannabimimetics Induce Acute Myocardial Infarction in Healthy Young People?Cells. 2022 Mar 28;11(7):1142. doi: 10.3390/cells11071142. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anandamide inhibits Theiler's virus induced VCAM-1 in brain endothelial cells and reduces leukocyte transmigration in a model of blood brain barrier by activation of CB(1) receptors.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Aug 18;8:102. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-102. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21851608 Free PMC article.
-
Endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors in ischaemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;153(2):252-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707582. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18026124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocannabinoid system in cardiovascular disorders - new pharmacotherapeutic opportunities.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2011 Jul;3(3):350-60. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.84435. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2011. PMID: 21966155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BAUERSACHS J., BOULOUMIE A., FRACCAROLLO D., HU K., BUSSE R., ERTL G. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic myocardial infarction despite increased vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase expression: role of enhanced vascular superoxide production. Circulation. 1999;100:292–298. - PubMed
-
- DEVANE W.A., HANUS L., BREUER A., PERTWEE R.G., STEVENSON L.A., GRIFF C., GIBSON D., MANDELBAUM A., ETINGER A., MECHOULAM R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science. 1992;258:1946–1949. - PubMed
-
- FLETCHER P.J., PFEFFER J.M., PFEFFER M.A., BRAUNWALD E. Left-ventricular diastolic pressure–volume relations in rats with healed myocardial infarction: effects on systolic function. Circ. Res. 1981;49:618–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

