Nonlinear accumulation in the brain of the new taxoid TXD258 following saturation of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier in mice and rats
- PMID: 12711638
- PMCID: PMC1573768
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705150
Nonlinear accumulation in the brain of the new taxoid TXD258 following saturation of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier in mice and rats
Abstract
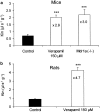
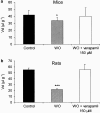
1. TXD258, a new taxoid antitumor agent, is a poor substrate for the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in Caco-2 cells. In this study, we investigated the amount of drug accumulating in the brains of rats and mice under a variety of conditions (dose and infusion time, species and plasma concentration) using conventional in vivo pharmacokinetic techniques and in situ brain perfusion. 2. Mice were infused with radiolabeled TXD258 at 15, 30, 45 and 90 mg m(-2) for 45 s or 1 h and rats were infused with 15 and 60 mg m(-2) over 2.3 min. The radioactivity in the plasma and brains was measured. The brain concentrations of TXD258 in mice and rats were maximal from 2 min to 1 h postinfusion and radioactivity was still detectable at 168 h. While the plasma concentration of TXD258 increased linearly in mice with the infused dose, the brain content increased more than proportionally with the dose between 15 and 90 mg m(-2). This nonlinear uptake of TXD258 also occurred in the plasma and brain of the rat. 3. These findings suggest that the protein-mediated efflux across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) becomes saturated. In situ brain perfusion studies confirmed that TXD258 is a P-gp substrate at the BBB of mice and rats. The P-gp of both species was saturated at the half-inhibitory concentration ( approximately 13 micro M) produced by i.v. infusion. 4 Thus, the observed nonlinear accumulation of TXD258 in the brain seems to occur by saturation of the P-gp at the rodent BBB. This saturation could have several advantages, such as overcoming a P-gp-mediated efflux, but the nonlinear pharmacokinetics could increase the risk of toxicity.
Figures




References
-
- ADACHI Y., SUZUKI H., SUGIYAMA Y. Comparative studies on in vitro methods for evaluating in vivo function of MDR1 P-glycoprotein. Pharma. Res. 2001;18:1660–1668. - PubMed
-
- AMBUDKAR S.V., DEY S., HRYCYNA C.A., RAMACHANDRA M., PASTAN I., GOTTESMAN M.M. Biochemical, cellular and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999;39:361–398. - PubMed
-
- BISSERY M.C., BOUCHARD H., RIOU J.F., VRIGNAUD C., COMBEAU J., BOURZAT J.D., COMMERCON A., LAVELLE F.Preclinical evaluation of TXD258, a new taxoid. Proceedings of the 91st American Association for Cancer Research 2000San Francisco, CA; 214April 1 – 541p
-
- BISSERY M.C., NOHYNEK G., SANDERINK G.J., LAVELLE F. Docetaxel (Taxotere): a review of preclinical and clinical experience. Part I: preclinical experience. Anticancer Drugs. 1995;6:339, 363–355. - PubMed
-
- CLARKE S.J., RIVORY L.P. Clinical pharmacokinetics of docetaxel. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999;36:99–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

