Molecular determinants of the cell-cycle regulated Mcm1p-Fkh2p transcription factor complex
- PMID: 12711672
- PMCID: PMC154233
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg347
Molecular determinants of the cell-cycle regulated Mcm1p-Fkh2p transcription factor complex
Abstract
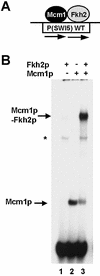
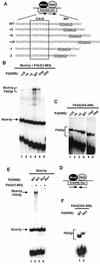
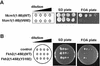
The MADS-box transcription factor Mcm1p and forkhead (FKH) transcription factor Fkh2p act in a DNA-bound complex to regulate cell-cycle dependent expression of the CLB2 cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Binding of Fkh2p requires prior binding by Mcm1p. Here we have investigated the molecular determinants governing the formation of the Mcm1p- Fkh2p complex. Fkh2p exhibits cooperativity in complex formation with Mcm1p and we have mapped a small region of Fkh2p located immediately upstream of the FKH DNA binding domain that is required for this cooperativity. This region is lacking in the related protein Fkh1p that cannot form ternary complexes with Mcm1p. A second region is identified that inhibits Mcm1p-independent DNA binding by Fkh2p. The spacing between the Mcm1p and Fkh2p binding sites is also a critical determinant for complex formation. We also show that Fkh2p can form ternary complexes with the human counterpart of Mcm1p, serum response factor (SRF). Mutations at analogous positions in Mcm1p, which are known to affect SRF interaction with its partner protein Elk-1, abrogate complex formation with Fkh2p, demonstrating evolutionary conservation of coregulatory protein binding surfaces. Our data therefore provide molecular insights into the mechanisms of Mcm1p- Fkh2p complex formation and more generally aid our understanding of MADS-box protein function.
Figures


References
-
- Dolan J.W. and Fields,S. (1991) Cell-type-specific transcription in yeast. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1088, 155–169. - PubMed
-
- Shore P. and Sharrocks,A.D. (1995) The MADS-box family of transcription factors. Eur. J. Biochem., 229, 1–13. - PubMed
-
- McInerny C.J., Partridge,J.F., Mikesell,G.E., Creemer,D.P. and Breeden,L.L. (1997) A novel Mcm1-dependent element in the SWI4, CLN3, CDC6, and CDC47 promoters activates M/G1-specific transcription. Genes Dev., 11, 1277–1288. - PubMed
-
- Breeden L.L. (2000) Cyclin transcription: timing is everything. Curr. Biol., 10, R586–588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

