Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins and cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins during osteophyte formation in humans
- PMID: 12713267
- PMCID: PMC1571079
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00158.x
Expression of bone morphogenetic proteins and cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins during osteophyte formation in humans
Abstract
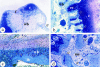
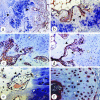
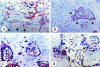
Bone- and cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins (BMPs and CDMPs), which are TGFbeta superfamily members, are growth and differentiation factors that have been recently isolated, cloned and biologically characterized. They are important regulators of key events in the processes of bone formation during embryogenesis, postnatal growth, remodelling and regeneration of the skeleton. In the present study, we used immunohistochemical methods to investigate the distribution of BMP-2, -3, -5, -6, -7 and CDMP-1, -2, -3 in human osteophytes (abnormal bony outgrowths) isolated from osteoarthritic hip and knee joints from patients undergoing total joint replacement surgery. All osteophytes consisted of three different areas of active bone formation: (1) endochondral bone formation within cartilage residues; (2) intramembranous bone formation within the fibrous tissue cover and (3) bone formation within bone marrow spaces. The immunohistochemistry of certain BMPs and CDMPs in each of these three different bone formation sites was determined. The results indicate that each BMP has a distinct pattern of distribution. Immunoreactivity for BMP-2 was observed in fibrous tissue matrix as well as in osteoblasts; BMP-3 was mainly present in osteoblasts; BMP-6 was restricted to young osteocytes and bone matrix; BMP-7 was observed in hypertrophic chondrocytes, osteoblasts and young osteocytes of both endochondral and intramembranous bone formation sites. CDMP-1, -2 and -3 were strongly expressed in all cartilage cells. Surprisingly, BMP-3 and -6 were found in osteoclasts at the sites of bone resorption. Since a similar distribution pattern of bone morphogenetic proteins was observed during embryonal bone development, it is suggested that osteophyte formation is regulated by the same molecular mechanism as normal bone during embryogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Aigner T, Dietz U, Stöβ H, von der Mark K. Differential expression of collagen types I, II, III, and X in human osteophytes. Lab. Invest. 1995;73:236–243. - PubMed
-
- Anderson HC, Hodges PT, Moylan PE. Bone morphogenetic protein expression by cells of human and rat growth plate, metaphysis and articular cartilage. J. Bone Mineral Res. 1999;14(Suppl. 1):5309.
-
- Anderson HC, Hodges PT, Aguilera XM, Missana L, Moylan PE. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) localization in developing human and rat growth plate, metaphysis, epiphysis and articular cartilage. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2000;48:1493–1502. - PubMed
-
- Aspenberg P, Basic N, Tagil M, Vukicevic S. Reduced expression of BMP-3 due to mechanical loading – A link between mechanical stimuli and tissue differentiation. Acta Orthopaedica Scand. 2000;71:558–562. - PubMed
-
- Bostrom MPG, Lane JM, Berberian WS, Missri AA, Tomin E, Weiland A, et al. Immunolocalization and expression of bone morphogenetic proteins-2 and -4 in fracture healing. J. Orthopaedic Res. 1995;13:357–367. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

