Drugs in development: bisphosphonates and metalloproteinase inhibitors
- PMID: 12716443
- PMCID: PMC154424
- DOI: 10.1186/ar604
Drugs in development: bisphosphonates and metalloproteinase inhibitors
Abstract
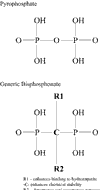
The destruction of bone and cartilage is characteristic of the progression of musculoskeletal diseases. The present review discusses the developments made with two different classes of drugs, the bisphosphonates and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Bisphosphonates have proven to be an effective and safe treatment for the prevention of bone loss, especially in osteoporotic disease, and may have a role in the treatment of arthritic diseases. The development of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and their role as potential therapies are also discussed, especially in the light of the disappointing human trials data so far published.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Bisphosphonates and combined treatments osteoporosis].Rev Med Suisse. 2005 Oct 5;1(35):2266, 2269-71. Rev Med Suisse. 2005. PMID: 16268449 French.
-
Metalloproteinase inhibitors: new opportunities for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2000 Jul;9(7):1469-78. doi: 10.1517/13543784.9.7.1469. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2000. PMID: 11060752 Review.
-
Bisphosphonates: mechanisms of action and clinical use in osteoporosis--an update.Horm Metab Res. 1997 Mar;29(3):145-50. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-979008. Horm Metab Res. 1997. PMID: 9137986 Review.
-
Effects of tetracyclines on bone metabolism.Adv Dent Res. 1998 Nov;12(2):56-62. doi: 10.1177/08959374980120012101. Adv Dent Res. 1998. PMID: 9972123 Review.
-
Biphenyl sulfonylamino methyl bisphosphonic acids as inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases and bone resorption.ChemMedChem. 2011 Jul 4;6(7):1258-68. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201000540. Epub 2011 Mar 15. ChemMedChem. 2011. PMID: 21714093
Cited by
-
Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016 Oct;12(10):580-92. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.136. Epub 2016 Aug 19. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27539668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calciphylaxis: Successful Management of a Rare Complication of Chronic Kidney Disease in Two Patients.Case Rep Nephrol. 2019 Jun 17;2019:1630613. doi: 10.1155/2019/1630613. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31316845 Free PMC article.
-
Targets, models and challenges in osteoarthritis research.Dis Model Mech. 2015 Jan;8(1):17-30. doi: 10.1242/dmm.016881. Dis Model Mech. 2015. PMID: 25561745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory biomarkers and state of the tibiofemoral joint in the osteoarthritic knee: a narrative review.Ann Jt. 2024 Jun 11;9:27. doi: 10.21037/aoj-23-59. eCollection 2024. Ann Jt. 2024. PMID: 39114418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mithramycin downregulates proinflammatory cytokine-induced matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in articular chondrocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(4):R777-83. doi: 10.1186/ar1735. Epub 2005 Apr 4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15987479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scott DL, Pugner K, Kaarela K, Doyle DV, Woolf A, Holmes J, Hieke K. The links between joint damage and disability in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2000;39:122–132. - PubMed
-
- Prockop DJ. What holds us together? Why do some of us fall apart? What can we do about it? Matrix Biol. 1998;16:519–528. - PubMed
-
- Hardingham TE, Fosang AJ. Proteoglycans – many forms and many functions. Faseb J. 1992;6:861–870. - PubMed
-
- Barrett AJ, Rawlings ND, Woessner JF. In Handbook of Protolytic Enzymes. London: Academic Press; 1998. Introduction. pp. xxv–xxix.
-
- Gravallese EM, Goldring SR. Cellular mechanisms and the role of cytokines in bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:2143–2151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

