Adult mesenchymal stem cells and cell-based tissue engineering
- PMID: 12716446
- PMCID: PMC154434
- DOI: 10.1186/ar614
Adult mesenchymal stem cells and cell-based tissue engineering
Abstract
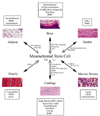
The identification of multipotential mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from adult human tissues, including bone marrow stroma and a number of connective tissues, has provided exciting prospects for cell-based tissue engineering and regeneration. This review focuses on the biology of MSCs, including their differentiation potentials in vitro and in vivo, and the application of MSCs in tissue engineering. Our current understanding of MSCs lags behind that of other stem cell types, such as hematopoietic stem cells. Future research should aim to define the cellular and molecular fingerprints of MSCs and elucidate their endogenous role(s) in normal and abnormal tissue functions.
Figures
References
-
- Lin H. The tao of stem cells in the germline. Annu Rev Genet. 1997;31:455–491. - PubMed
-
- de Wynter EA, Emmerson AJ, Testa NG. Properties of peripheral blood and cord blood stem cells. Baillière's Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 1999;12:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Dua HS, Azuara-Blanco A. Limbal stem cells of the corneal epithelium. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000;44:415–425. - PubMed
-
- Rao MS. Multipotent and restricted precursors in the central nervous system. Anat Rec. 1999;257:137–148. - PubMed
-
- Lagasse E, Connors H, Al-Dhalimy M, Reitsma M, Dohse M, Osborne L, Wang X, Finegold M, Weissman IL, Grompe M. Purified hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate into hepatocytes in vivo. Nature Med. 2000;6:1229–1234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

