Autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage repair: monitoring its success by magnetic resonance imaging and histology
- PMID: 12716454
- PMCID: PMC154433
- DOI: 10.1186/ar613
Autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage repair: monitoring its success by magnetic resonance imaging and histology
Abstract
Autologous chondrocyte implantation is being used increasingly for the treatment of cartilage defects. In spite of this, there has been a paucity of objective, standardised assessment of the outcome and quality of repair tissue formed. We have investigated patients treated with autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI), some in conjunction with mosaicplasty, and developed objective, semiquantitative scoring schemes to monitor the repair tissue using MRI and histology. Results indicate repair tissue to be on average 2.5 mm thick. It was of varying morphology ranging from predominantly hyaline in 22% of biopsy specimens, mixed in 48%, through to predominantly fibrocartilage, in 30%, apparently improving with increasing time postgraft. Repair tissue was well integrated with the host tissue in all aspects viewed. MRI scans provide a useful assessment of properties of the whole graft area and adjacent tissue and is a noninvasive technique for long-term follow-up. It correlated with histology (P = 0.02) in patients treated with ACI alone.
Figures

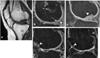


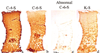

References
-
- Buckwalter JA. Articular cartilage: injuries and potential for healing. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1998;28:192–202. - PubMed
-
- Minas T, Nehrer S. Current concepts in the treatment of articular cartilage defects. Orthopedics. 1997;20:525–536. - PubMed
-
- Jobanputra P, Parry D, Fry-Smith A, Burls A. Effectiveness of autologous chondrocyte transplantation for hyaline cartilage defects in knee. Health Technology Assessment. 2001;5:1–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

