Intravitreal gene therapy reduces lysosomal storage in specific areas of the CNS in mucopolysaccharidosis VII mice
- PMID: 12716937
- PMCID: PMC6742327
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-08-03302.2003
Intravitreal gene therapy reduces lysosomal storage in specific areas of the CNS in mucopolysaccharidosis VII mice
Abstract
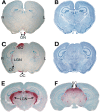
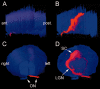
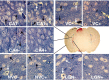
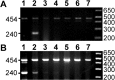
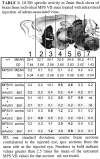
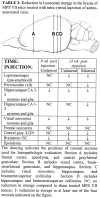
The mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs) are lysosomal storage diseases resulting from impaired catabolism of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. MPS VII mice lack lysosomal beta-glucuronidase (GUSB) activity, leading to the accumulation of partially degraded chondroitin, dermatan, and heparan sulfates in most tissues. Consequently, these mice develop most of the symptoms exhibited by human MPS VII patients, including progressive visual and cognitive deficits. To investigate the effects of reducing lysosomal storage in nervous tissues, we injected recombinant adeno-associated virus encoding GUSB directly into the vitreous humor of young adult mice. Interestingly, GUSB activity was subsequently detected in the brains of the recipients. At 8-12 weeks after treatment, increased GUSB activity and reduced lysosomal distension were found in regions of the thalamus and tectum that received inputs from the injected eye. Lysosomal storage was also reduced in adjacent nonvisual regions, including the hippocampus, as well as in the visual cortex. The findings suggest that both diffusion and trans-synaptic transfer contribute to the dissemination of enzyme activity within the CNS. Intravitreal injection may thus provide a means of delivering certain therapeutic gene products to specific areas within the CNS.
Figures
References
-
- Bosch A, Ferret E, Desmaris N, Trono D, Heard JM. Reversal of pathology in the entire brain of mucopolysaccharidosis type VII mice after lentivirus-mediated gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther. 2000;11:1139–1150. - PubMed
-
- Brooks AI, Stein CS, Hughes SM, Heth J, McCray PM, Jr, Sauter SL, Johnston JC, Cory-Slechta DA, Federoff HJ, Davidson BL. Functional correction of established central nervous system deficits in an animal model of lysosomal storage disease with feline immunodeficiency virus-based vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:6216–6221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Daly T, Okuyama T, Vogler C, Haskins M, Muzyczka N, Sands MS. Neonatal intramuscular injection with recombinant adeno-associated virus results in prolonged β-glucuronidase expression in situ and correction of liver pathology in mucopolysaccharidosis type VII mice. Hum Gene Ther. 1999a;10:85–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
