Epidermal growth factor receptors control competence to interpret leukemia inhibitory factor as an astrocyte inducer in developing cortex
- PMID: 12716946
- PMCID: PMC6742320
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-08-03385.2003
Epidermal growth factor receptors control competence to interpret leukemia inhibitory factor as an astrocyte inducer in developing cortex
Abstract
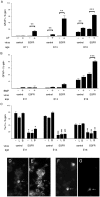
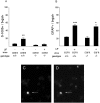
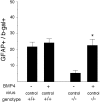
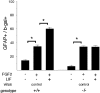
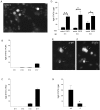
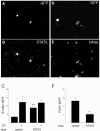
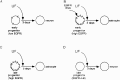
Cortical progenitors begin to interpret leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) as astrocyte-inducing signals during late embryonic cortical development, coincident with an increase in their expression of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFRs). To determine whether the developmental change in EGFRs regulates the change in responsiveness to LIF and BMP, we analyzed cortical progenitors induced to express EGFRs prematurely and progenitors from late embryonic EGFR-null cortex. Premature elevation of EGFRs conferred premature competence to interpret LIF, but not BMP, as an astrocyte-inducing signal. EGFR-null progenitors from late embryonic cortex did not interpret LIF as an astrocyte-inducing signal but responded to BMP4. LIF responsiveness in EGFR-null cells was rescued by the addition of EGFRs but not by the stimulation of fibroblast growth factor receptors. Astrocyte differentiation induced by LIF depends on signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). We show that the level of STAT3 increases during late embryonic development in a subset of progenitors. EGFRs regulate this change in STAT3 and increase STAT3 phosphorylation in response to LIF. Increasing STAT3 prematurely with a retrovirus also increased the phosphorylation of STAT3 by LIF. In contrast to the finding with EGFRs, however, increasing STAT3 did not cause LIF to induce astrocytes, although it reduced expression of the neurogenic factor PAX6 (paired box gene 6 ). Our findings show that developmental changes in EGFRs regulate the competence of progenitors to interpret LIF as an astrocyte-inducing signal. EGFRs elevate STAT3 expression and increase its phosphorylation by LIF, but this is not sufficient to change LIF responsiveness to astrocyte induction, suggesting that EGFRs also regulate LIF responsiveness downstream of STAT3.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signaling crosstalk underlying synergistic induction of astrocyte differentiation by BMPs and IL-6 family of cytokines.FEBS Lett. 2001 Feb 2;489(2-3):139-43. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02095-6. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11165238
-
Synergistic signaling in fetal brain by STAT3-Smad1 complex bridged by p300.Science. 1999 Apr 16;284(5413):479-82. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5413.479. Science. 1999. PMID: 10205054
-
BMP induction of Id proteins suppresses differentiation and sustains embryonic stem cell self-renewal in collaboration with STAT3.Cell. 2003 Oct 31;115(3):281-92. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00847-x. Cell. 2003. PMID: 14636556
-
Pathways regulating lens induction in the mouse.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(8-9):783-91. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041903rl. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15558471 Review.
-
PACAP signaling to DREAM: a cAMP-dependent pathway that regulates cortical astrogliogenesis.Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Apr;39(2):90-100. doi: 10.1007/s12035-009-8055-2. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19238593 Review.
Cited by
-
PML represses lung cancer metastasis by suppressing the nuclear EGFR-mediated transcriptional activation of MMP2.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(19):3132-42. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.949212. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486572 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent effect of EGF on migration and differentiation of adult subventricular zone astrocytes.Glia. 2010 Jun;58(8):975-83. doi: 10.1002/glia.20979. Glia. 2010. PMID: 20187143 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired neural stem cell expansion and hypersensitivity to epileptic seizures in mice lacking the EGFR in the brain.FEBS J. 2018 Sep;285(17):3175-3196. doi: 10.1111/febs.14603. Epub 2018 Aug 4. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 30028091 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor promotes murine enteric nervous system development and enteric neural crest cell migration.J Pediatr Surg. 2012 Oct;47(10):1865-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2012.05.008. J Pediatr Surg. 2012. PMID: 23084199 Free PMC article.
-
Neuron-astroglial interactions in cell-fate commitment and maturation in the central nervous system.Neurochem Res. 2012 Nov;37(11):2402-18. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0798-x. Epub 2012 May 22. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22614925 Review.
References
-
- Bayer SA, Altman J. Neocortical development. Raven; New York: 1991.
-
- Bonni A, Sun Y, Nadal-Vicens M, Bhatt A, Frank DA, Rozovsky I, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD, Greenberg ME. Regulation of gliogenesis in the central nervous system by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Science. 1997;278:477–483. - PubMed
-
- Burrows RC, Wancio D, Levitt P, Lillien L. Response diversity and the timing of progenitor cell maturation are regulated by developmental changes in EGFR expression in the cortex. Neuron. 1997;19:251–267. - PubMed
-
- Caric D, Raphael H, Viti J, Feathers A, Wancio D, Lillien L. EGFRs mediate chemotactic migration in the developing telencephalon. Development. 2001;128:4203–4216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
