Roles of conformational stability and colloidal stability in the aggregation of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
- PMID: 12717013
- PMCID: PMC2323861
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0235703
Roles of conformational stability and colloidal stability in the aggregation of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
Abstract
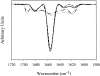
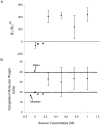
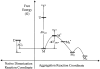
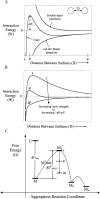
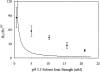
We studied the non-native aggregation of recombinant human granulocyte stimulating factor (rhGCSF) in solution conditions where native rhGCSF is both conformationally stable compared to its unfolded state and at concentrations well below its solubility limit. Aggregation of rhGCSF first involves the perturbation of its native structure to form a structurally expanded transition state, followed by assembly process to form an irreversible aggregate. The energy barriers of the two steps are reflected in the experimentally measured values of free energy of unfolding (DeltaG(unf)) and osmotic second virial coefficient (B(22)), respectively. Under solution conditions where rhGCSF conformational stability dominates (i.e., large DeltaG(unf) and negative B(22)), the first step is rate-limiting, and increasing DeltaG(unf) (e.g., by the addition of sucrose) decreases aggregation. In solutions where colloidal stability is high (i.e., large and positive B(22) values) the second step is rate-limiting, and solution conditions (e.g., low pH and low ionic strength) that increase repulsive interactions between protein molecules are effective at reducing aggregation. rhGCSF aggregation is thus controlled by both conformational stability and colloidal stability, and depending on the solution conditions, either could be rate-limiting.
Figures
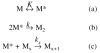
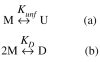
References
-
- Atkins, P. 1994. Physical chemistry, 5th ed., p. 1031. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York.
-
- B.I. Corporation. 1993. Instrument manual for BI-ZP software, version 4.0 & higher and BI-9025AT & BI-2025AT signal processors, version 1.1.b. Holtsville, NY.
-
- Chang, R.C., Asthagiri, D., and Lenhoff, A.M. 2000. Measured and calculated effects of mutations in bacteriophage T4 lysozyme on interactions in solution. Proteins 41 123–132. - PubMed
-
- Dong, A.C., Meyer, J.D., Brown, J.L., Manning, M.C., and Carpenter, J.F. 2000. Comparative Fourier transform infrared and circular dichroism spectroscopic analysis of α(1)-proteinase inhibitor and ovalbumin in aqueous solution. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 383 148–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

