Response of human REV3 gene to gastric cancer inducing carcinogen N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine and its role in mutagenesis
- PMID: 12717825
- PMCID: PMC4611392
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.888
Response of human REV3 gene to gastric cancer inducing carcinogen N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine and its role in mutagenesis
Abstract
Aim: To understand the response of human REV3 gene to gastric cancer inducing carcinogen N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) and its role in human mutagenesis.
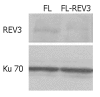
Methods: The response of the human REV3 gene to MNNG was measured in human 293 cells and FL cells by RT-PCR. By using antisense technology, mutation analysis at HPRT locus (on which lesion-targeted mutation usually occurs) was conducted in human transgenic cell line FL-REV3(-) by 8-azaguanine screening, and mutation occurred on undamaged DNA template was detected by using a shuttle plasmid pZ189 as the probe in human transgenic cell lines 293-REV3(-) and FL-REV3(-). The blockage effect of REV3 was measured by combination of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction to detect the expression of antisense REV3 RNA and Western blotting to detect the REV3 protein level.
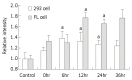
Results: The human REV3 gene was significantly activated by MNNG treatment, as indicated by the upregulation of REV3 gene expression at the transcriptional level in MNNG-treated human cells, with significant increase of REV3 expression level by 0.38 fold, 0.33 fold and 0.27 fold respectively at 6 h, 12 h and 24 h in MNNG-treated 293 cells (P<0.05); and to 0.77 fold and 0.65 fold at 12 h and 24 h respectively in MNNG-treated FL cells (P<0.05). In transgenic cell line (in which REV3 was blocked by antisense REV3 RNA), high level of antisense REV3 RNA was detected, with a decreased level of REV3 protein. MNNG treatment significantly increased the mutation frequencies on undamaged DNA template (untargeted mutation), and also at HPRT locus (lesion-targeted mutation). However, when REV3 gene was blocked by antisense REV3 RNA, the MNNG-induced mutation frequency on undamaged DNA templates was significantly decreased by 3.8 fold (P<0.05) and 5.8 fold (P<0.01) respectively both in MNNG-pretreated transgenic 293 cells and FL cells in which REV3 was blocked by antisense RNA, and almost recovered to their spontaneous mutation levels. The spontaneous HPRT mutation was disappeared in REV3-disrupted cells, and induced mutation frequency at HPRT locus significantly decreased from 8.66 x 10(-6) in FL cells to 0.14 x 10(-6) in transgenic cells as well (P<0.01).
Conclusion: The expression of the human REV3 can be upregulated at the transcriptional level in response to MNNG. The human REV3 gene plays a role not only in lesion-targeted DNA mutagenesis, but also in mutagenesis on undamaged DNA templates that is called untargeted mutation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA polymerase zeta: new insight into eukaryotic mutagenesis and mammalian embryonic development.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jun;9(6):1165-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1165. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12800216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Cloning and bioinformatics of human REV3 gene promoter region and its response to carcinogen N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2003 Oct;32(5):393-7. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2003.05.006. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2003. PMID: 14610737 Chinese.
-
Response of REV3 promoter to N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine.Mutat Res. 2004 Jun 4;550(1-2):49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.02.006. Mutat Res. 2004. PMID: 15135640
-
Decreased frequency and highly aberrant spectrum of ultraviolet-induced mutations in the hprt gene of mouse fibroblasts expressing antisense RNA to DNA polymerase zeta.Mol Cancer Res. 2003 Sep;1(11):836-47. Mol Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14517346
-
Genetic effects of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine and its homologs.Mutat Res. 1982 Sep;99(2):129-242. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(82)90057-4. Mutat Res. 1982. PMID: 6750393 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA polymerase zeta: new insight into eukaryotic mutagenesis and mammalian embryonic development.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Jun;9(6):1165-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i6.1165. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12800216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Participation of translesion synthesis DNA polymerases in the maintenance of chromosome integrity in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011 Jan;76(1):49-60. doi: 10.1134/s000629791101007x. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011. PMID: 21568839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stenius U, Högberg J. Re: Yang, J. and Duerksen-Hughes, P. (1998) A new approach to identifying genotoxic carcinogens: p53 induction as an indicator of genotoxic damage. Carcinogenesis, 19, 1117-1125. Carcinogenesis. 1999;20:181–182. - PubMed
-
- Mortality trends for selected smoking-related cancers and breast cancer--United States, 1950-1990. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1993;42:857, 863–866. - PubMed
-
- Bollschweiler E, Hölscher AH. [Carcinoma of the esophagus--actual epidemiology in Germany] Onkologie. 2001;24:180–184. - PubMed
-
- Bonnin-Scaon S, Lafon P, Chasseigne G, Mullet E, Sorum PC. Learning the relationship between smoking, drinking alcohol and the risk of esophageal cancer. Health Educ Res. 2002;17:415–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

