Imbalance between expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in invasiveness and metastasis of human gastric carcinoma
- PMID: 12717827
- PMCID: PMC4611394
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.899
Imbalance between expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in invasiveness and metastasis of human gastric carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: The expressive balance between matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) plays a critical role in maintaining the degradation and synthesis of extracellular matrix. Loss of such balance is associated with invasion and metastasis of tumors. This study aimed to determine the expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in gastric carcinoma, and the association of the expressive imbalance between MMP-9 and TIMP-1 with the invasion and metastasis and prognosis of gastric carcinoma.
Methods: We used immunohistochemistry to determine the expressions of MMP-9, TIMP-1 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen Ki-67 in the gastric specimens taken from 256 patients with primary gastric carcinoma. The patients were followed-up for up to 96 months.
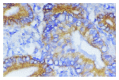
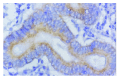
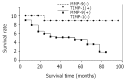
Results: No association between the expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 and patients' sex and age, tumor size and location of gastric carcinoma was observed. The incidence of the positive expression of MMP-9 in cases with tumors invasion to muscularis propria and visceral peritoneum (70.13 % and 69.09 %, respectively) was significantly higher than that in cases with tumor invasion only to lamina propria or submucosa (42.50 %, P=0.0162). The positive correlation between MMP-9 expression and the depth of tumor invasion was observed (Pearson correlation coefficient=0.2129, P=0.016). Along with the increase of the metastatic station of lymph nodes, the incidence of the MMP-9 expression was increased by degrees; a positive correlation between them was observed (Pearson correlation coefficient=0.2910, P=0.0001). There was also a significant correlation between MMP-9 expression and the TNM stage in gastric carcinoma (Pearson correlation coefficient=0.3027, P<0.0001). The incidence of MMP-9 expression in stage II and III/IV (75.00 % and 76.15 %, respectively) was significantly higher than those in stage I (46.15 %, P<0.0001). A negative correlation between TIMP-1 immunoreactivity and the depth of invasion, status of lymph node metastasis and TNM stage was observed (Pearson correlation coefficient =-0.1688, -0.3556 and -0.3004, P=0.023, <0.0001 and <0.0001, respectively). Four types of co-expression of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 were observed; i.e. MMP-9 positive but TIMP-1 negative (n=115), both positive (n=52), both negative (n=62) and MMP-9 negative but TIMP-1 positive (n=27). The frequency of serosal invasiveness was significant higher in patients with MMP-9 but without TIMP-1 expression than those with other types of the co-expression (P=0.0303). The incidence of lymph node metastasis was highest in patients with MMP-9 but without TIMP-1 expression, and lowest in those with TIMP-1 but without MMP-9 expression (P<0.0001). The survival rate in patients with MMP-9 but without TIMP-1 expression was lower than that in those with TIMP-1 but without MMP-9 expression (P=0.0014).
Conclusion: Our results in gastric carcinoma demonstrated a significant positive association of MMP-9 over-expression with proliferation of tumor cells, the depth of invasiveness, lymph node metastasis and TNM stage, suggesting MMP-9 can serve as a molecular marker of tumor invasion and metastasis. We also demonstrate a significant negative relationship of TIMP-1 expression with the depth of invasiveness and lymph node metastasis, which provide a new idea in the tumor biological and genetic treatment. The interaction between MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in the processes of tumor invasion and metastasis is that MMP-9 mainly promotes tumor invasion and metastasis and TIMP-1 inhibits functions of MMP-9. The imbalance between MMP-9 and TIMP-1 expression may suggest the occurrence of tumor invasion and metastasis, predict poor prognosis. For patients with imbalanced MMP-9 and TIMP-1 expression, the optimal treatment scheme needs to be selected.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Relationship of expression unbalance of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase to invasiveness and metastasis in gastric carcinomas].Ai Zheng. 2002 Mar;21(3):305-10. Ai Zheng. 2002. PMID: 12452001 Chinese.
-
DNA ploidy analysis and expression of MMP-9, TIMP-2, and E-cadherin in gastric carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Sep 28;11(36):5592-600. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i36.5592. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16237750 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of twist and matrix metalloproteinase-9 with metastasis and prognosis in gastric cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9):5055-60. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.9.5055. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24175775
-
Prognostic Impact of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 in Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(42):7694-7713. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180904114455. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30182835
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of TIMP1 expression in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024 Nov;24(11):1169-1176. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2024.2408278. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 39305243
Cited by
-
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 Is Confined to Tumor-Associated Myofibroblasts and Is Increased With Progression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma.J Histochem Cytochem. 2016 Aug;64(8):483-94. doi: 10.1369/0022155416656173. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Histochem Cytochem. 2016. PMID: 27370797 Free PMC article.
-
THE ROLE OF SERUM CK-18, MMP-9 AND TIPM-1 LEVELS IN PREDICTING R0 RESECTION IN PATIENTS WITH GASTRIC CANCER.Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2018 Dec 6;31(4):e1401. doi: 10.1590/0102-672020180001e1401. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2018. Retraction in: Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2020 Nov 20;33(2):e1531. doi: 10.1590/0102-672020200002e1531. PMID: 30539976 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Ds-echinoside A, a new triterpene glycoside derived from sea cucumber, exhibits antimetastatic activity via the inhibition of NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 and VEGF expressions.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2011 Jul;12(7):534-44. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1000217. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2011. PMID: 21726060 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of tumor-related molecular expression in gastric carcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2009 Dec;15(4):589-96. doi: 10.1007/s12253-009-9158-9. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Pathol Oncol Res. 2009. PMID: 19294533
-
Implication of gelatinases in retinoblastoma development.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2016 Apr-Jun;60(2):68-70. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 29450326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aznavoorian S, Murphy AN, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Liotta LA. Molecular aspects of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer. 1993;71:1368–1383. - PubMed
-
- Nagase H, Woessner JF. Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:21491–21494. - PubMed
-
- Westermarck J, Kähäri VM. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. FASEB J. 1999;13:781–792. - PubMed
-
- Ellenrieder V, Adler G, Gress TM. Invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Ann Oncol. 1999;10 Suppl 4:46–50. - PubMed
-
- Yoshizaki T, Sato H, Furukawa M. Recent advances in the regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation: from basic research to clinical implication (Review) Oncol Rep. 2002;9:607–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

