Synergistic effects of nimesulide and 5-fluorouracil on tumor growth and apoptosis in the implanted hepatoma in mice
- PMID: 12717833
- PMCID: PMC4611400
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.936
Synergistic effects of nimesulide and 5-fluorouracil on tumor growth and apoptosis in the implanted hepatoma in mice
Abstract
Aim: To compare the effect of nimesulide or/and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) on tumor growth inhibition and apoptosis in mice with the implanted hepatoma and to observe their possible interactions.
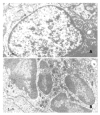
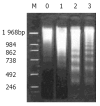
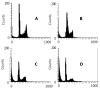
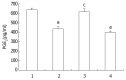
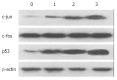
Methods: The inhibitory effects on tumor growth was evaluated by inhibition rate. Apoptosis was assessed by the ultrastructural, flow cytometry features and the DNA ladder demonstrated by agarose gel electrophoresis. PGE(2) level was determined by radioimmunoassay. Expression levels of c-jun, c-fos and p53 were evaluated by western blotting.
Results: Nimesulide or 5-FU alone inhibited the growth of hepatoma, while a synergistic effect was observed for a combined use of both. More pronounced morphologic changes for tumor cell apoptosis and the DNA ladder were found for the latter treatment. Expression levels of c-jun and p53 were found to be elevated for the tumors from mice treated with nimesulide and 5-FU comparing to those with either of them, but a reduced PGE(2) level was observed only for the treatment with nimesulide. No change was detected on c-fos expression.
Conclusion: Nimesulide and 5-FU appear to have synergistic effects for the growth inhibition and apoptosis induction. Both were found to be overexpressed in p53 and c-jun proteins, rather than that of c-fos, associations with the resulted apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nimesulide inhibits tumor growth in mice implanted hepatoma: overexpression of Bax over Bcl-2.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003 Oct;24(10):1045-50. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003. PMID: 14531950
-
Synergistic effect of 5-fluorouracil and the flavanoid oroxylin A on HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma and on H22 transplanted mice.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010 Feb;65(3):481-9. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-1053-2. Epub 2009 Jul 8. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19585117
-
The effect of calmodulin antagonist berbaminederivative-EBB on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo.Chin Med J (Engl). 2002 May;115(5):759-62. Chin Med J (Engl). 2002. PMID: 12133551
-
Synergistic effect of triptolide combined with 5-fluorouracil on colon carcinoma.Postgrad Med J. 2007 May;83(979):338-43. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.2006.055426. Postgrad Med J. 2007. PMID: 17488865 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by rofecoxib attenuates the growth and metastatic potential of colorectal carcinoma in mice.Cancer Res. 2003 Feb 1;63(3):586-92. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12566300
Cited by
-
The Protective Effects of Ciji-Hua'ai-Baosheng II Formula on Chemotherapy-Treated H22 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mouse Model by Promoting Tumor Apoptosis.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 8;9:1539. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01539. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30670974 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of endogenous nitric oxide induced by 5-fluorouracil and L-Arg on liver carcinoma in nude mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Dec 14;13(46):6249-53. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i46.6249. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 18069768 Free PMC article.
-
Low expression of the dynamic network markers FOS/JUN in pre-deteriorated epithelial cells is associated with the progression of colorectal adenoma to carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2023 Jan 25;21(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03890-5. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36698183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoneda K, Yamamoto T, Osaki T. p53- and p21-independent apoptosis of squamous cell carcinoma cells induced by 5-fluorouracil and radiation. Oral Oncol. 1998;34:529–537. - PubMed
-
- Warr JR, Bamford A, Quinn DM. The preferential induction of apoptosis in multidrug-resistant KB cells by 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Lett. 2002;175:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Mizutani Y, Nakanishi H, Yoshida O, Fukushima M, Bonavida B, Miki T. Potentiation of the sensitivity of renal cell carcinoma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by subtoxic concentrations of 5-fluorouracil. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:167–176. - PubMed
-
- Fukushima M, Fujioka A, Uchida J, Nakagawa F, Takechi T. Thymidylate synthase (TS) and ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) may be involved in acquired resistance to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in human cancer xenografts in vivo. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37:1681–1687. - PubMed
-
- Grem JL, Nguyen D, Monahan BP, Kao V, Geoffroy FJ. Sequence-dependent antagonism between fluorouracil and paclitaxel in human breast cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;58:477–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

