Signal transduction of gap junctional genes, connexin32, connexin43 in human hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 12717835
- PMCID: PMC4611402
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.946
Signal transduction of gap junctional genes, connexin32, connexin43 in human hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate gap junctional intercellular communication (GJIC) in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines, and signal transduction mechanism of gap junction genes connexin32(cx32),connexin43(cx43) in human hepatocarcinogenesis.
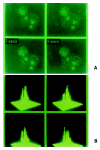
Methods: Scarped loading and dye transfer (SLDT) was employed with Lucifer Yellow (LY) to detect GJIC function in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines HHCC, SMMC-7721 and normal control liver cell line QZG. After Fluo-3AM loading, laser scanning confocal microscope (LSCM) was used to measure concentrations of intracellular calcium (Ca(2+))i in the cells. The phosphorylation on tyrosine of connexin proteins was examined by immunoblot.
Results: SLDT showed that ability of GJIC function was higher in QZG cell than that in HHCC and SMMC-7721 cell lines. By laser scanning confocal microscopy, concentrations of intracellular free calcium (Ca(2+))i was much higher in QZG cell line (108.37 nmol/L) than those in HHCC (35.13 nmol/L) and SMMC-7721 (47.08 nmol/L) cells. Western blot suggested that only QZG cells had unphosphorylated tyrosine in Cx32 protein of 32 ku and Cx43 protein of 43 ku; SMMC-7721 cells showed phosphorylated tyrosine Cx43 protein.
Conclusion: The results indicated that carcinogenesis and development of human hepatocellular carcinoma related with the abnormal expression of cx genes and disorder of its signal transduction pathway, such as decrease of (Ca(2+))i, post-translation phosphorylation on tyrosine of Cx proteins which led to a dramatic disruption of GJIC.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of gap junction genes connexin32 and connexin43 mRNAs and proteins, and their role in hepatocarcinogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Feb;8(1):64-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.64. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 11833073 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of all-trans retinoic acid on expression of connexin genes and gap junction communication in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Jun 1;85(20):1414-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16029656 Chinese.
-
[Decreased expression of Cx32 and Cx43 and their function of gap junction intercellular communication in gastric cancer].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2007 Oct;29(10):742-7. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18396685 Chinese.
-
Role of gap junctions in lung neoplasia.Exp Lung Res. 1998 Jul-Aug;24(4):523-39. doi: 10.3109/01902149809087384. Exp Lung Res. 1998. PMID: 9659581 Review.
-
[Intra- and intercellular Ca(2+)-signal transduction].Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2000;62(6):501-63. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2000. PMID: 11196579 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of continuous positive airway pressure on TNF-α in obstructive sleep apnea patients: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 23;18(3):e0282172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282172. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36952521 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional responses of liver and spleen in Lota lota to polyriboinosinic polyribocytidylic acid.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 13;14:1272393. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1272393. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37901224 Free PMC article.
-
Are gap junction gene connexins 26, 32 and 43 of prognostic values in hepatocellular carcinoma? A prospective study.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Oct 1;10(19):2785-90. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2785. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15334670 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

