The mRNA expression patterns of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and TNFR-I in some vital organs after thermal injury
- PMID: 12717852
- PMCID: PMC4611368
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i5.1038
The mRNA expression patterns of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and TNFR-I in some vital organs after thermal injury
Abstract
Aim: To investigate changes of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and TNFR-I expression in vital organs and their significance in the pathogenesis of multiple organ damage associated with endogenous endotoxin following major burns.
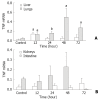
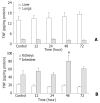
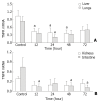
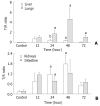
Methods: Wistar rats subjected to a 35 % full-thickness scald injury were sacrificed at 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h postburn, respectively. Meanwhile, eight rats were taken as normal controls. Tissue samples from liver, spleen, kidney, lung and intestine were collected to assay tissue endotoxin levels and measure TNF-alpha and TNFR-I expression. In addition, blood samples were obtained for the determination of organ function parameters.
Results: Endotoxin levels in liver, spleen and lung increased markedly after thermal injury, with the highest level in liver. The gene expression of TNF-alpha in liver, lung and kidney was up-regulated after thermal injury, while the TNFR-I mRNA expression in liver, lung, kidney and intestine was shown decreased throughout the observation period. Thus, the mRNA expression ratio of TNF-alpha to TNFR-I was significantly increased postburn, particularly in pulmonary tissue (67-fold). In addition, the significant correlations between the expression of TNFR-I or the expression ratio of TNF-alpha/TNFR mRNA in liver tissue and serum aspartate aminotransferase levels were noted (P<0.05-0.01). Similar results were also obtained between pulmonary TNF-alpha mRNA expression and myeloperoxidase activities (P<0.01), whereas there was a highly negative correlation between levels of renal TNFR-I mRNA expression and serum creatinine.
Conclusion: Burn injury could result in the translocation of gut-derived endotoxin that was mainly distributed in the liver, spleen and lung. The translocated endotoxin then made the expression of TNF-alpha and TNFR-I mRNA up-regulated and down-regulated respectively in various organs, which might be involved in the pathogenesis of multiple organ damage following burns.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effects of extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibition by AG126 on tissue tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression and multiple organ dysfunction in rats with postburn Staphylococcus aureus sepsis].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004 Apr 7;42(7):391-5. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15144664 Chinese.
-
The significance of changes in high mobility group-1 protein mRNA expression in rats after thermal injury.Shock. 2002 Apr;17(4):329-33. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200204000-00016. Shock. 2002. PMID: 11954836
-
[Gene expression of lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rats after thermal injury].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1999 May;37(5):271-3. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1999. PMID: 11829837 Chinese.
-
[Induction mechanism of shock: applying the etiology in judgment of the cause of death in forensic practice].Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 2004 Sep;58(2):130-40. Nihon Hoigaku Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15526767 Review. Japanese.
-
On the role of tumor necrosis factor and receptors in models of multiorgan failure, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease.Immunol Rev. 1999 Jun;169:175-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01315.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10450517 Review.
Cited by
-
The Probable Protective Effect of Photobiomodulation on the Inflammation of the Airway and Lung in COVID-19 Treatment: A Preclinical and Clinical Meta-Analysis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1376:29-44. doi: 10.1007/5584_2021_665. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 34907516
-
Protective Effects of Melatonin against Severe Burn-Induced Distant Organ Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Experimental Studies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Nov 27;9(12):1196. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121196. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33261180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Burn-Induced Multiple Organ Injury and Protective Effect of Lutein in Rats.Inflammation. 2018 Jun;41(3):760-772. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0730-x. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29417308
References
-
- Yao YM, Redl H, Bahrami S, Schlag G. The inflammatory basis of trauma/shock-associated multiple organ failure. Inflamm Res. 1998;47:201–210. - PubMed
-
- Swank GM, Deitch EA. Role of the gut in multiple organ failure: bacterial translocation and permeability changes. World J Surg. 1996;20:411–417. - PubMed
-
- Fang WH, Yao YM, Shi ZG, Yu Yan, Wu Ye, Lu LR, Sheng ZY. The effect of recombinant bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein on endotoxin translocation and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein/CD14 expression in rats following thermal injury. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1452–1459. - PubMed
-
- Fang CW, Yao YM, Shi ZG, Yu Y, Wu Y, Lu LR, Sheng ZY. Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14 gene expression after thermal injury and its potential mechanism(s) J Trauma. 2002;53:957–967. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

