Intra-articular hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) and hylans for the treatment of osteoarthritis: mechanisms of action
- PMID: 12718745
- PMCID: PMC165033
- DOI: 10.1186/ar623
Intra-articular hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) and hylans for the treatment of osteoarthritis: mechanisms of action
Abstract
Although the predominant mechanism of intra-articular hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) (HA) and hylans for the treatment of pain associated with knee osteoarthritis (OA) is unknown, in vivo, in vitro, and clinical studies demonstrate various physiological effects of exogenous HA. HA can reduce nerve impulses and nerve sensitivity associated with the pain of OA. In experimental OA, this glycosaminoglycan has protective effects on cartilage, which may be mediated by its molecular and cellular effects observed in vitro. Exogenous HA enhances chondrocyte HA and proteoglycan synthesis, reduces the production and activity of proinflammatory mediators and matrix metalloproteinases, and alters the behavior of immune cells. Many of the physiological effects of exogenous HA may be a function of its molecular weight. Several physiological effects probably contribute to the mechanisms by which HA and hylans exert their clinical effects in knee OA.
Figures

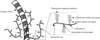
References
-
- Balazs E. The physical properties of synovial fluid and the specific role of hyaluronic acid. In: Helfet AJ, editor. In Disorders of the Knee. Philadelphia: J B Lippincott; 1982. pp. 61–74.
-
- Adams ME, Atkinson MH, Lussier AJ, Schulz JI, Siminovitch KA, Wade JP, Zummer M. The role of viscosupplementation with hylan G-F 20 (Synvisc) in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a Canadian multicenter trial comparing hylan G-F 20 alone, hylan G-F 20 with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and NSAIDs alone. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1995;3:213–225. - PubMed
-
- Lussier A, Cividino AA, McFarlane CA, Olszynski WP, Potashner WJ, De Medicis R. Viscosupplementation with hylan for the treatment of osteoarthritis: findings from clinical practice in Canada. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:1579–1585. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

