Role of the dielectric constants of membrane proteins and channel water in ion permeation
- PMID: 12719220
- PMCID: PMC1302851
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)70015-0
Role of the dielectric constants of membrane proteins and channel water in ion permeation
Abstract
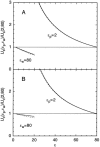
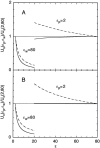
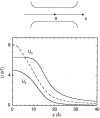
Using both analytical solutions obtained from simplified systems and numerical results from more realistic cases, we investigate the role played by the dielectric constant of membrane proteins epsilon(p) and pore water epsilon(w) in permeation of ions across channels. We show that the boundary and its curvature are the crucial factors in determining how an ion's potential energy depends on the dielectric constants near an interface. The potential energy of an ion outside a globular protein has a dominant 1/epsilon(w) dependence, but this becomes 1/epsilon(p) for an ion inside a cavity. For channels, where the boundaries are in between these two extremes, the situation is more complex. In general, we find that variations in epsilon(w) have a much larger impact on the potential energy of an ion compared to those in epsilon(p). Therefore a better understanding of the effective epsilon(w) values employed in channel models is desirable. Although the precise value of epsilon(p) is not a crucial determinant of ion permeation properties, it still needs to be chosen carefully when quantitative comparisons with data are made.
Figures





References
-
- Allen, T. W., S. Kuyucak, and S. H. Chung. 1999. The effect of hydrophobic and hydrophilic channel walls on the structure and diffusion of water and ions. J. Chem. Phys. 111:7985–7999.
-
- Allen, T. W., S. Kuyucak, and S. H. Chung. 2000. Molecular dynamics estimates of ion diffusion in model hydrophobic and the KcsA potassium channels. Biophys. Chem. 86:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Burykin, A., C. N. Schutz, J. Villa, and A. Warshel. 2002. Simulations of ion current in realistic models of ion channels: the KcsA potassium channel. Proteins. 47:265–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

