Stimulatory action of internal protons on Slo1 BK channels
- PMID: 12719228
- PMCID: PMC1302859
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)70023-X
Stimulatory action of internal protons on Slo1 BK channels
Abstract
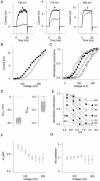
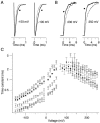
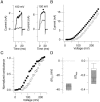
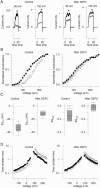
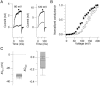
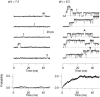
We investigated the internal pH-sensitivity of heterologously expressed hSlo1 BK channels. In the virtual absence of Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) to isolate the voltage-dependent gating transitions, low internal pH enhanced macroscopic hSlo1 currents by shifting the voltage-dependence of activation to more negative voltages. The activation time course was faster and the deactivation time course was slower with low pH. The estimated K(d) value of the stimulatory effect was approximately pH = 6.5 or 0.35 micro M. The stimulatory effect was maintained when the auxiliary subunit mouse beta1 was coexpressed. Treatment of the hSlo1 channel with the histidine modifying agent diethyl pyrocarbonate also enhanced the hSlo1 currents and greatly diminished the internal pH sensitivity, suggesting that diethyl pyrocarbonate and low pH may work on the same effector mechanism. High concentrations of Ca(2+) or Mg(2+) also masked the stimulatory effect of low internal pH. These results indicate that the acid-sensitivity of the Slo BK channel may involve the channel domain implicated in the divalent-dependent activation.
Figures
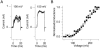


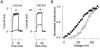


References
-
- Adelman, J. P., K. Z. Shen, M. P. Kavanaugh, R. A. Warren, Y. N. Wu, A. Lagrutta, C. T. Bond, and R. A. North. 1992. Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron. 9:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Brenner, R., T. J. Jegla, A. Wickenden, Y. Liu, and R. W. Aldrich. 2000a. Cloning and functional characterization of novel large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel beta subunits, hKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4. J. Biol. Chem. 275:6453–6461. - PubMed
-
- Brenner, R., G. J. Perez, A. D. Bonev, D. M. Eckman, J. C. Kosek, S. W. Wiler, A. J. Patterson, M. T. Nelson, and R. W. Aldrich. 2000b. Vasoregulation by the beta1 subunit of the calcium-activated potassium channel. Nature. 407:870–876. - PubMed
-
- Butler, A., S. Tsunoda, D. P. McCobb, A. Wei, and L. Salkoff. 1993. mSlo, a complex mouse gene encoding “maxi” calcium-activated potassium channels. Science. 261:221–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

