Helicobacter pylori CagA protein targets the c-Met receptor and enhances the motogenic response
- PMID: 12719469
- PMCID: PMC2172921
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200208039
Helicobacter pylori CagA protein targets the c-Met receptor and enhances the motogenic response
Abstract
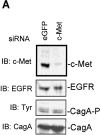
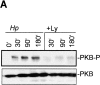
Infection with the human microbial pathogen Helicobacter pylori is assumed to lead to invasive gastric cancer. We find that H. pylori activates the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor c-Met, which is involved in invasive growth of tumor cells. The H. pylori effector protein CagA intracellularly targets the c-Met receptor and promotes cellular processes leading to a forceful motogenic response. CagA could represent a bacterial adaptor protein that associates with phospholipase Cgamma but not Grb2-associated binder 1 or growth factor receptor-bound protein 2. The H. pylori-induced motogenic response is suppressed and blocked by the inhibition of PLCgamma and of MAPK, respectively. Thus, upon translocation, CagA modulates cellular functions by deregulating c-Met receptor signaling. The activation of the motogenic response in H. pylori-infected epithelial cells suggests that CagA could be involved in tumor progression.
Figures














References
-
- Backert, S., E. Ziska, V. Brinkmann, U. Zimny-Arndt, A. Fauconnier, P.R. Jungblut, M. Naumann, and T.F. Meyer. 2000. Translocation of the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein in gastric epithelial cells by a type IV secretion apparatus. Cell Microbiol. 2:155–164. - PubMed
-
- Bardelli, A., P. Longati, D. Gramaglia, C. Basilico, L. Tamagnone, S. Giordano, D. Ballinari, P. Michieli, and P.M. Comoglio. 1998. Uncoupling signal transducers from oncogenic MET mutants abrogates cell transformation and inhibits invasive growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95:14379–14383. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carpenter, G., and Q. Ji. 1999. Phospholipase C-gamma as a signal-transducing element. Exp. Cell Res. 253:15–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

