The hepatitis C virus p7 protein forms an ion channel that is inhibited by long-alkyl-chain iminosugar derivatives
- PMID: 12719519
- PMCID: PMC156333
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1031527100
The hepatitis C virus p7 protein forms an ion channel that is inhibited by long-alkyl-chain iminosugar derivatives
Abstract
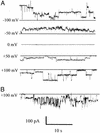
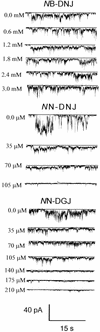
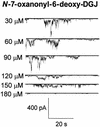
We show that hepatitis C virus (HCV) p7 protein forms ion channels in black lipid membranes. HCV p7 ion channels are inhibited by long-alkyl-chain iminosugar derivatives, which have antiviral activity against the HCV surrogate bovine viral diarrhea virus. HCV p7 presents a potential target for antiviral therapy.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

