Two major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted epitopes of the Borna disease virus p10 protein identified by cytotoxic T lymphocytes induced by DNA-based immunization
- PMID: 12719601
- PMCID: PMC154008
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.10.6076-6081.2003
Two major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted epitopes of the Borna disease virus p10 protein identified by cytotoxic T lymphocytes induced by DNA-based immunization
Abstract
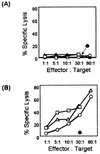
Borna disease virus (BDV) infection of Lewis rats is the most studied animal model of Borna disease, an often fatal encephalomyelitis. In this experimental model, BDV-specific CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) play a prominent role in the immunopathogenesis of infection by the noncytolytic, persistent BDV. Of the six open reading frames of BDV, CTLs to BDV X (p10) and the L-polymerase have never been studied. In this study, we used plasmid immunization to investigate the CTL response to BDV X and N. Plasmid-based immunization was a potent CTL inducer in Lewis rats. Anti-X CTLs were primed by a single injection of the p10 cDNA. Two codominant p10 epitopes, M(1)SSDLRLTLL(10) and T(8)LLELVRRL(16), associated with the RT1.A(l) major histocompatibility complex class I molecules of the Lewis rats, were identified. In addition, immunization with a BDV p40-expressing plasmid confirmed the previously reported RT1.A(l)-restricted A(230)SYAQMTTY(238) peptide as the CTL target for BDV N. In contrast to the CTL responses, plasmid vaccination was a poor inducer of an antibody response to p10. Three injections of a recombinant eukaryotic expression plasmid of BDV p10 were needed to generate a weak anti-p10 immunoglobulin M response. However, the antibody response could be optimized by a protein boost after priming with cDNA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of the immunodominant H-2K(k)-restricted cytotoxic T-cell epitope in the Borna disease virus nucleoprotein.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8579-88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8579-8588.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507203 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-induced protection against Borna disease in wild-type and perforin-deficient mice.J Gen Virol. 2005 Feb;86(Pt 2):399-403. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.80566-0. J Gen Virol. 2005. PMID: 15659759
-
Borna disease virus nucleoprotein (p40) is a major target for CD8(+)-T-cell-mediated immune response.J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1715-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1715-1718.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9882386 Free PMC article.
-
The immunopathogenesis of Borna disease virus infection.Front Biosci. 2002 Feb 1;7:d541-55. doi: 10.2741/A793. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 11815301 Review.
-
Borna disease virus infection in animals and humans.Emerg Infect Dis. 1997 Jul-Sep;3(3):343-52. doi: 10.3201/eid0303.970311. Emerg Infect Dis. 1997. PMID: 9284379 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevention of virus persistence and protection against immunopathology after Borna disease virus infection of the brain by a novel Orf virus recombinant.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(1):314-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.314-325.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15596826 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB results in impaired borna disease virus replication.J Virol. 2005 May;79(10):6043-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.10.6043-6051.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15857990 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a universal multi-epitope protein vaccine candidate for enhanced borna virus pandemic preparedness.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 5;15:1427677. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427677. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39703502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert, M. L., B. Sauter, and N. Bhardwaj. 1998. Dendritic cells acquire antigen from apoptotic cells and induce class I-restricted CTLs. Nature 392:86-89. - PubMed
-
- Bilzer, T., and L. Stitz. 1994. Immune-mediated brainatrophy. CD8+ T cells contribute to tissue destruction during Borna disease. J. Immunol. 153:818-823. - PubMed
-
- Bode, L., W. Zimmerman, R. Ferszt, F. Steinbach, and H. Ludwig. 1995. Borna disease virus genome transcribed and expressed in psychiatric patients. Nat. Med. 1:232-236. - PubMed
-
- Bode, L., R. Durrwald, F. A. Rantam, R. Ferszt, and H. Ludwig. 1996. First isolates of infectious human Borna disease virus from patients with mood disorders. Mol. Psych. 1:200-212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

