AT1 receptor antagonist therapy preferentially ameliorated right ventricular function and phenotype during the early phase of remodeling post-MI
- PMID: 12721104
- PMCID: PMC1573810
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705212
AT1 receptor antagonist therapy preferentially ameliorated right ventricular function and phenotype during the early phase of remodeling post-MI
Abstract
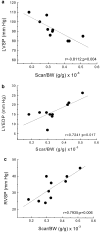
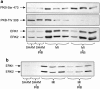
1. The influence of AII on contractile dysfunction, regulation of the tyrosine kinase-dependent signaling molecule extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and natriuretic peptide gene expression were examined in the noninfarcted left ventricle (NILV) and right ventricle (RV) during the early phase of remodeling post-myocardial infarct (MI) in the rat. The selective AT(1) receptor antagonist irbesartan was administered <10 h following coronary artery ligation, and rats were killed either at 4-day or 2-week post-MI. 2. At 4 days post-MI, left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP: sham=125+/-12, MI=91+/-4 mmHg) was decreased, whereas left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP: sham=9+/-2, MI=17+/-2 mm Hg), right ventricular systolic (RVSP: sham=26+/-1, MI=34+/-2 mm Hg), and end-diastolic pressures (RVEDP: sham=3+/-0.5, MI=7+/-1 mm Hg) were increased. ERK phosphorylation was significantly elevated in the NILV and RV. 3. Irbesartan (40 mg x kg(-1)/day(-1)) administration did not improve left ventricular function, or suppress increased ERK phosphorylation in the 4-day post-MI rat. By contrast, irbesartan therapy normalized RVSP (MI+irbesartan=25+/-1 mm Hg), RVEDP (MI+irbesartan=3+/-0.3 mm Hg), and reduced ERK1 (MI=3.0+/-0.6, MI+irbesartan=2.0+/-0.3-fold increase), and ERK2 (MI=3.8+/-0.8, MI+irbesartan=2.2+/-0.5-fold increase) phosphorylation. 4. In 2-week post-MI rats, biventricular dysfunction was associated with increased prepro-ANP, and prepro-BNP mRNA expression. Irbesartan therapy normalized RVSP, attenuated RVEDP, and abrogated natriuretic peptide mRNA expression (prepro-ANP; MI=9+/-2, MI+irbesartan=2+/-1-fold increase, prepro-BNP; MI=6+/-2, MI+irbesartan=1+/-1-fold increase), whereas both transcripts remained elevated in the NILV despite the partial attenuation of LVEDP. 5. These data suggest that the therapeutic benefit of irbesartan treatment during the early phase of remodeling post-MI was associated with the preferential amelioration of RV contractile function and phenotype.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonism with irbesartan inhibits ventricular hypertrophy and improves diastolic function in the remodeling post-myocardial infarction ventricle.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1999 Mar;33(3):433-9. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199903000-00014. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10069680
-
Additive amelioration of left ventricular remodeling and molecular alterations by combined aldosterone and angiotensin receptor blockade after myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Jul 1;67(1):97-105. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.03.001. Epub 2005 Apr 7. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15949473
-
[Effects of combination therapy with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin 1 receptor antagonist on ventricular remodeling and expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Apr 20;85(15):1053-6. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16029550 Chinese.
-
AT1 receptor blockade prevents cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction in rats.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2005 Aug;19(4):251-9. doi: 10.1007/s10557-005-3695-6. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2005. PMID: 16193242
-
Loss of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 accelerates maladaptive left ventricular remodeling in response to myocardial infarction.Circ Heart Fail. 2009 Sep;2(5):446-55. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.108.840124. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Circ Heart Fail. 2009. PMID: 19808375
Cited by
-
Tamoxifen treatment of myocardial infarcted female rats exacerbates scar formation.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Jun;454(3):385-93. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0215-5. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17285298
-
Antagonism of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha reduces infarct size and improves ventricular function after myocardial infarction.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Nov;455(2):241-50. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0284-5. Epub 2007 May 23. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17520275
-
Assessment and treatment of right ventricular failure.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013 Apr;10(4):204-18. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.12. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23399974 Review.
References
-
- AMBROSE J., PRIBNOW D.G., GIRAUD G.D., PERKINS K.D., MULDOON L., GREENBERG B.H. Angiotensin Type1 receptor antagonism with irbesartan inhibits ventricular hypertrophy and improves diastolic function in the remodeling post-myocardial infarction ventricle. J. Cardiovas. Pharmacol. 1999;33:433–439. - PubMed
-
- BELICHARD P., SAVARD P., CARDINAL R., NADEAU R., GOSSELIN H., PARADIS P., ROULEAU J.L. Markedly different effects on ventricular remodelling result in a decrease in inducibility of ventricular arrhythmias. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1994;23:505–513. - PubMed
-
- BOOZ G.W., DOSTAL D.E., SINGER H.A., BAKER K.M. Involvement of protein kinase C and Ca2+ in angiotensin II-induced mitogenesis of cardiac fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. 1994;267:C1308–C1318. - PubMed
-
- BUENO O.F., DE WINDT L.J., LIM H.W., TYMITZ K.M., WITT S.A., KIMBALL T.R., MOLKENTIN J.D. The dual-specificity phosphatase MKP-1 limits the cardiac hypertrophic response in vitro and in vivo. Circ. Res. 2001;88:88–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

