Sequence analysis of the N, P, M and F genes of Canadian human metapneumovirus strains
- PMID: 12727342
- PMCID: PMC7172423
- DOI: 10.1016/s0168-1702(03)00065-0
Sequence analysis of the N, P, M and F genes of Canadian human metapneumovirus strains
Abstract
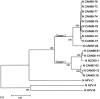
The complete nucleotide sequences of the nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), matrix protein (M), and fusion protein (F) genes of 15 Canadian human metapneumovirus (hMPV) isolates were determined. Phylogenetic analysis revealed two distinct genetic clusters, or groups for each gene with additional sequence variability within the individual groups. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences for the N, M and F genes of the different isolates revealed that all three genes were well conserved with 94.1-97.6% identity between the two distinct clusters The P gene showed more diversity with 81.6-85.7% amino acid identity for isolates between the two clusters, and 94.6-100% for isolates within the same cluster.
Figures






References
-
- Barr J., Chambers P., Pringle C.R., Easton A.J. Sequence of the major nucleocapsid protein gene of pneumonia virus of mice: sequence comparisons suggest structural homology between nucleocapsid proteins of pneumoviruses, paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses and filoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1991;72(Pt 3):677–685. - PubMed
-
- Bayon-Auboyer M.H., Arnauld C., Toquin D., Eterradossi N.’. Nucleotide sequences of the F, L and G protein genes of two non-A/non-B avian pneumoviruses (APV) reveal a novel APV subgroup. J. Gen. Virol. 2000;81:2723–2733. - PubMed
-
- Buckland R., Wild F.’. Leucine zipper motif extends. Nature. 1989;338:547. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

