An H-bond between two residues from different loops of the acetylcholine binding site contributes to the activation mechanism of nicotinic receptors
- PMID: 12727867
- PMCID: PMC156069
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg197
An H-bond between two residues from different loops of the acetylcholine binding site contributes to the activation mechanism of nicotinic receptors
Abstract
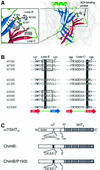
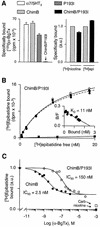
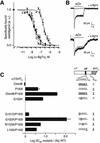
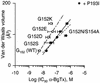
The molecular mechanisms of nicotinic receptor activation are still largely unknown. The crystallographic structure of the acetylcholine binding protein (AChBP) reveals a single H-bond between two different acetylcholine binding loops. Within these homologous loops we systematically introduced alpha4 residues into the alpha7/5HT(3) chimeric receptor and found that the single point mutations G152K (loop B) and P193I (loop C) displayed a non-additive increase of equilibrium binding affinity for several agonists compared with the double mutant G152K/P193I. In whole-cell patch-clamp recordings, G152K, P193I and G152K/P193I mutants displayed an increase up to 5-fold in acetylcholine potency with a large decrease of the apparent Hill coefficients (significantly smaller than one). Concomitantly, the G152K/P193I mutant showed a dramatic loss of high-affinity alpha-bungarotoxin binding (100-fold decrease), thus pinpointing a new contact area for the toxin. Fitting the data with an allosteric-kinetic model, together with molecular dynamic simulations, suggests that the presence of the inter-backbone H-bond between positions 152 and 193, revealed in alpha4 and in alpha7 double mutant but not in alpha7, coincides with a large stabilization of both open and desensitized states of nicotinic receptors.
Figures




References
-
- Brejc K., van Dijk,W.J., Klaassen,R., Schuurmans,M., van der Oost,J., Smit,A.B. and Sixma,T.K. (2001) Crystal structure of AChBP reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature, 411, 269–276. - PubMed
-
- Carter P.J., Winter,G., Wilkinson,A.J. and Fersht,A.R. (1984) The use of double mutants to detect structural changes in the active site of the tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (Bacillus stearothermophilus). Cell, 38, 835–840. - PubMed
-
- Case D.A. et al. (2002) AMBER 7. University of California, San Francisco, CA.
-
- Cheng Y.C. and Prusoff,W.H. (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50% inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol., 22, 3099–3108. - PubMed
-
- Corringer P.J., Galzi,J.-L., Eisele,J.-L., Bertrand,S., Changeux,J.-P. and Bertrand,D. (1995) Identification of a new component of the agonist binding site of the nicotinic α7 homooligomeric receptor. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 11749–11752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

