Genome-wide in silico identification of transcriptional regulators controlling the cell cycle in human cells
- PMID: 12727897
- PMCID: PMC430898
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.947203
Genome-wide in silico identification of transcriptional regulators controlling the cell cycle in human cells
Abstract
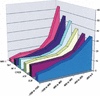
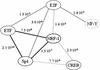
Dissection of regulatory networks that control gene transcription is one of the greatest challenges of functional genomics. Using human genomic sequences, models for binding sites of known transcription factors, and gene expression data, we demonstrate that the reverse engineering approach, which infers regulatory mechanisms from gene expression patterns, can reveal transcriptional networks in human cells. To date, such methodologies were successfully demonstrated only in prokaryotes and low eukaryotes. We developed computational methods for identifying putative binding sites of transcription factors and for evaluating the statistical significance of their prevalence in a given set of promoters. Focusing on transcriptional mechanisms that control cell cycle progression, our computational analyses revealed eight transcription factors whose binding sites are significantly overrepresented in promoters of genes whose expression is cell-cycle-dependent. The enrichment of some of these factors is specific to certain phases of the cell cycle. In addition, several pairs of these transcription factors show a significant co-occurrence rate in cell-cycle-regulated promoters. Each such pair indicates functional cooperation between its members in regulating the transcriptional program associated with cell cycle progression. The methods presented here are general and can be applied to the analysis of transcriptional networks controlling any biological process.
Figures
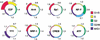
References
-
- Berman B.P., Nibu, Y., Pfeiffer, B.D., Tomancak, P., Celniker, S.E., Levine, M., Rubin, G.M., and Eisen, M.B. 2002. Exploiting transcription factor binding site clustering to identify cis-regulatory modules involved in pattern formation in the Drosophila genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99: 757-762. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cram E.J., Liu, B.D., Bjeldanes, L.F., and Firestone, G.L. 2001. Indole-3-carbinol inhibits CDK6 expression in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells by disrupting Sp1 transcription factor interactions with a composite element in the CDK6 gene promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 22332-22340. - PubMed
-
- Crowe D.L. and Shemirani, B. 2000. The transcription factor ATF-2 inhibits extracellular signal regulated kinase expression and proliferation of human cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 20: 2945-2949. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
