MPR
- PMID: 12729968
- PMCID: PMC2724598
- DOI: 10.1016/s0376-6357(03)00017-2
MPR
Abstract
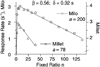
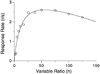
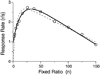
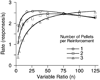
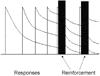
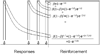
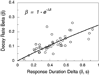
Mathematical Principles of Reinforcement (MPR) is a theory of reinforcement schedules. This paper reviews the origin of the principles constituting MPR: arousal, association and constraint. Incentives invigorate responses, in particular those preceding and predicting the incentive. The process that generates an associative bond between stimuli, responses and incentives is called coupling. The combination of arousal and coupling constitutes reinforcement. Models of coupling play a central role in the evolution of the theory. The time required to respond constrains the maximum response rates, and generates a hyperbolic relation between rate of responding and rate of reinforcement. Models of control by ratio schedules are developed to illustrate the interaction of the principles. Correlations among parameters are incorporated into the structure of the models, and assumptions that were made in the original theory are refined in light of current data.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Theory of reinforcement schedules.J Exp Anal Behav. 2023 Nov;120(3):289-319. doi: 10.1002/jeab.880. Epub 2023 Sep 14. J Exp Anal Behav. 2023. PMID: 37706228 Review.
-
Extending mathematical principles of reinforcement into the domain of behavioral pharmacology.Behav Processes. 2003 Apr 28;62(1-3):75-88. doi: 10.1016/s0376-6357(03)00027-5. Behav Processes. 2003. PMID: 12729970
-
Mathematical principles of reinforcement and resistance to change.Behav Processes. 2003 Apr 28;62(1-3):65-73. doi: 10.1016/s0376-6357(03)00018-4. Behav Processes. 2003. PMID: 12729969
-
Effects of SKF-83566 and haloperidol on performance on progressive ratio schedules maintained by sucrose and corn oil reinforcement: quantitative analysis using a new model derived from the Mathematical Principles of Reinforcement (MPR).Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Dec;230(4):617-30. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3189-3. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23828157 Free PMC article.
-
A theory of behaviour on progressive ratio schedules, with applications in behavioural pharmacology.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Aug;222(4):549-64. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2771-4. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22752382 Review.
Cited by
-
Early-life seizures produce lasting alterations in the structure and function of the prefrontal cortex.Epilepsy Behav. 2011 Oct;22(2):214-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2011.07.022. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Epilepsy Behav. 2011. PMID: 21873119 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin signaling via the orexin 1 receptor mediates operant responding for food reinforcement.Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Apr 15;67(8):753-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.12.035. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20189166 Free PMC article.
-
Using rodent data to elucidate dopaminergic mechanisms of ADHD: Implications for human personality.Personal Neurosci. 2024 Jan 31;7:e2. doi: 10.1017/pen.2023.12. eCollection 2024. Personal Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38384667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ensuring Effective Public Health Communication: Insights and Modeling Efforts From Theories of Behavioral Economics, Heuristics, and Behavioral Analysis for Decision Making Under Risk.Front Psychol. 2021 Oct 13;12:715159. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.715159. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34721162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting the Next Response: Demonstrating the Utility of Integrating Artificial Intelligence-Based Reinforcement Learning with Behavior Science.Perspect Behav Sci. 2025 Apr 30;48(2):241-267. doi: 10.1007/s40614-025-00444-6. eCollection 2025 Jun. Perspect Behav Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520581
References
-
- Bharucha-Reid AT. Elements of the theory of Markov processes and their applications. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1960.
-
- Bizo LA, Kettle LC, Killeen PR. Rats don’t always respond faster for more food: the paradoxical incentive effect. Anim. Learn. Behav. 2001;29:66–78.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

