Early colonization events in the mutualistic association between Steinernema carpocapsae nematodes and Xenorhabdus nematophila bacteria
- PMID: 12730175
- PMCID: PMC154081
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.10.3147-3154.2003
Early colonization events in the mutualistic association between Steinernema carpocapsae nematodes and Xenorhabdus nematophila bacteria
Abstract
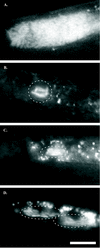
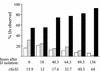
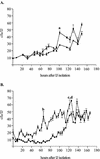
The bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophila is a mutualist of the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae. During its life cycle, the bacterium exists both separately from the nematode and as an intestinal resident of a nonfeeding nematode form, the infective juvenile (IJ). The progression of X. nematophila from an ex vivo existence to a specific and persistent colonization of IJs is a model to understand the mechanisms mediating the initiation and maintenance of benign host-microbe interactions. To help characterize this process, we constructed an X. nematophila strain that constitutively expresses green fluorescent protein, which allowed its presence to be monitored within IJs. Using this strain, we showed that few bacterial cells initiate colonization of an individual IJ and that these grow inside the lumen of the IJ intestine in a reproducible polyphasic pattern during colonization. In accordance with these two observations, we demonstrated that the final population of bacteria in a nematode is of predominantly monoclonal origin, suggesting that only one or two bacterial clones initiate or persist during colonization of an individual nematode. These data suggest that X. nematophila initiates IJ colonization by competing for limited colonization sites or resources within the nematode intestine. This report represents the first description of the biological interactions occurring between X. nematophila and S. carpocapsae during the early stages of the colonization process, provides insights into the physiology of X. nematophila in its host niche, and will facilitate interpretation of future data regarding the molecular events mediating this process.
Figures

References
-
- Aballay, A., and F. M. Ausubel. 2002. Caenorhabditis elegans as a host for the study of host-pathogen interactions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 5:97-101. - PubMed
-
- Akhurst, R. J. 1983. Neoaplectana species: specificity of association with bacteria of the genus Xenorhabdus. Exp. Parasitol. 55:258-263. - PubMed
-
- Akhurst, R. J., and N. Boemare. 1990. Biology and taxonomy of Xenorhabdus, p. 75-87. In R. Gaugler and H. K. Kaya (ed.), Entomopathogenic nematodes in biological control. CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Fla.
-
- Ausubel, F. A., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1998. Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley and Sons, New York, N.Y.
-
- Bao, Y., D. P. Lies, H. Fu, and G. P. Roberts. 1991. An improved Tn7-based system for the single-copy insertion of cloned genes into chromosomes of gram-negative bacteria. Gene 109:167-168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

