Wavelet to predict bacterial ori and ter: a tendency towards a physical balance
- PMID: 12732098
- PMCID: PMC156607
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-4-17
Wavelet to predict bacterial ori and ter: a tendency towards a physical balance
Abstract
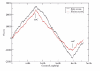
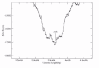
Background: Chromosomal DNA replication in bacteria starts at the origin (ori) and the two replicores propagate in opposite directions up to the terminus (ter) region. We hypothesize that the two replicores need to reach ter at the same time to maintain a physical balance; DNA insertion would disrupt such a balance, requiring chromosomal rearrangements to restore the balance. To test this hypothesis, we needed to demonstrate that ori and ter are in a physical balance in bacterial chromosomes. Using wavelet analysis, we documented GC skew, AT skew, purine excess and keto excess on the published bacterial genomic sequences to locate the turning (minimum and maximum) points on the curves. Previously, the minimum point had been supposed to correlate with ori and the maximum to correlate with ter.
Results: We observed a strong tendency of the bacterial chromosomes towards a physical balance, with the minima and maxima corresponding to the known or putative ori and ter and being about half chromosome separated in most of the bacteria studied. A nonparametric method based on wavelet transformation was employed to perform significance tests for the predicted loci.
Conclusions: The wavelet approach can reliably predict the ori and ter regions and the bacterial chromosomes have a strong tendency towards a physical balance between ori and ter.
Figures








References
-
- Bird RE, Louarn J, Martuscelli J, Caro L. Origin and sequence of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972;70:549–566. - PubMed
-
- Hill TM, Pelletier AJ, Tecklenburg ML, Kuempel PL. Identification of the DNA sequence from the E. coli terminus region that halts replication forks. Cell. 1988;55:459–466. - PubMed
-
- Hidaka M, Akiyama M, Horiuchi T. A consensus sequence of three DNA replication terminus sites on the E. coli chromosome is highly homologous to the terR sites of the R6K plasmid. Cell. 1988;55:467–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

